Hybrid gene selection approach using XGBoost and multi-objective genetic algorithm for cancer classification
Paper and Code
May 30, 2021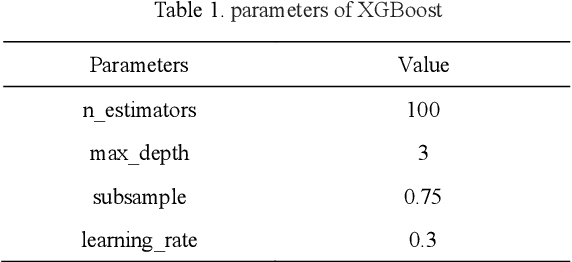



Microarray gene expression data are often accompanied by a large number of genes and a small number of samples. However, only a few of these genes are relevant to cancer, resulting in signigicant gene selection challenges. Hence, we propose a two-stage gene selection approach by combining extreme gradient boosting (XGBoost) and a multi-objective optimization genetic algorithm (XGBoost-MOGA) for cancer classification in microarray datasets. In the first stage, the genes are ranked use an ensemble-based feature selection using XGBoost. This stage can effectively remove irrelevant genes and yield a group comprising the most relevant genes related to the class. In the second stage, XGBoost-MOGA searches for an optimal gene subset based on the most relevant genes's group using a multi-objective optimization genetic algorithm. We performed comprehensive experiments to compare XGBoost-MOGA with other state-of-the-art feature selection methods using two well-known learning classifiers on 13 publicly available microarray expression datasets. The experimental results show that XGBoost-MOGA yields significantly better results than previous state-of-the-art algorithms in terms of various evaluation criteria, such as accuracy, F-score, precision, and recall.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge