Human-Robot Handshaking: A Review
Paper and Code
Feb 14, 2021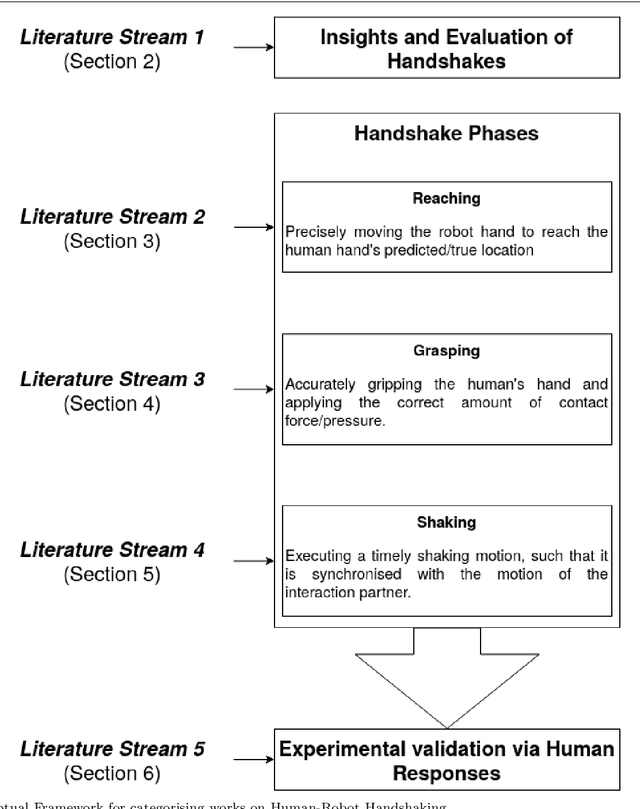
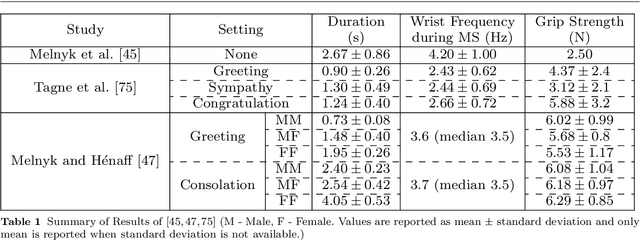
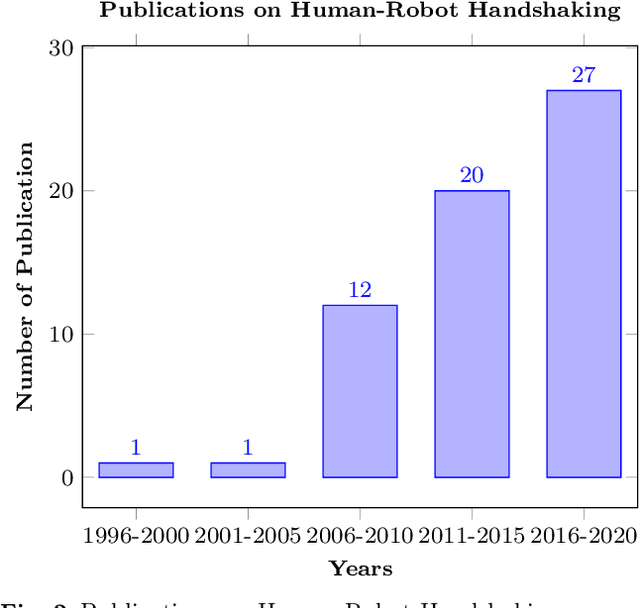
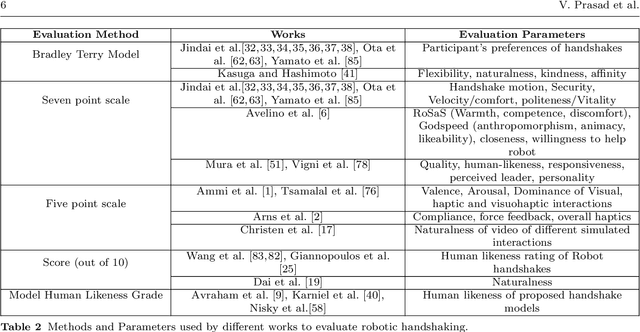
For some years now, the use of social, anthropomorphic robots in various situations has been on the rise. These are robots developed to interact with humans and are equipped with corresponding extremities. They already support human users in various industries, such as retail, gastronomy, hotels, education and healthcare. During such Human-Robot Interaction (HRI) scenarios, physical touch plays a central role in the various applications of social robots as interactive non-verbal behaviour is a key factor in making the interaction more natural. Shaking hands is a simple, natural interaction used commonly in many social contexts and is seen as a symbol of greeting, farewell and congratulations. In this paper, we take a look at the existing state of Human-Robot Handshaking research, categorise the works based on their focus areas, draw out the major findings of these areas while analysing their pitfalls. We mainly see that some form of synchronisation exists during the different phases of the interaction. In addition to this, we also find that additional factors like gaze, voice facial expressions etc. can affect the perception of a robotic handshake and that internal factors like personality and mood can affect the way in which handshaking behaviours are executed by humans. Based on the findings and insights, we finally discuss possible ways forward for research on such physically interactive behaviours.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge