How to Boost Face Recognition with StyleGAN?
Paper and Code
Oct 18, 2022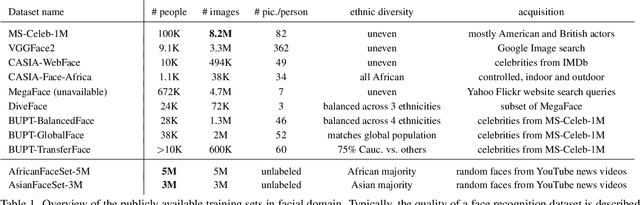
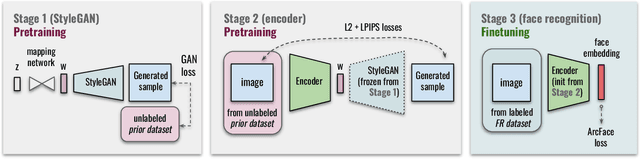
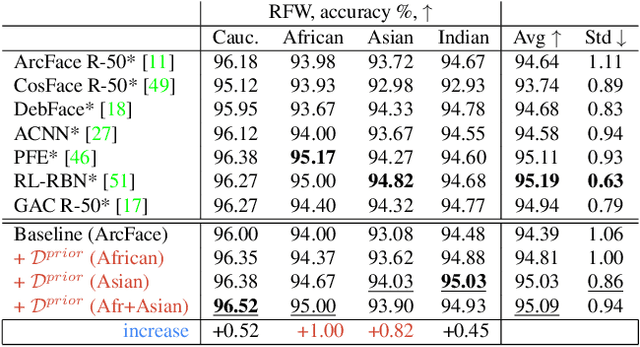
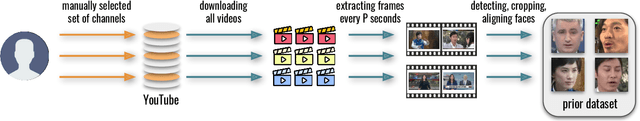
State-of-the-art face recognition systems require huge amounts of labeled training data. Given the priority of privacy in face recognition applications, the data is limited to celebrity web crawls, which have issues such as skewed distributions of ethnicities and limited numbers of identities. On the other hand, the self-supervised revolution in the industry motivates research on adaptation of the related techniques to facial recognition. One of the most popular practical tricks is to augment the dataset by the samples drawn from the high-resolution high-fidelity models (e.g. StyleGAN-like), while preserving the identity. We show that a simple approach based on fine-tuning an encoder for StyleGAN allows to improve upon the state-of-the-art facial recognition and performs better compared to training on synthetic face identities. We also collect large-scale unlabeled datasets with controllable ethnic constitution -- AfricanFaceSet-5M (5 million images of different people) and AsianFaceSet-3M (3 million images of different people) and we show that pretraining on each of them improves recognition of the respective ethnicities (as well as also others), while combining all unlabeled datasets results in the biggest performance increase. Our self-supervised strategy is the most useful with limited amounts of labeled training data, which can be beneficial for more tailored face recognition tasks and when facing privacy concerns. Evaluation is provided based on a standard RFW dataset and a new large-scale RB-WebFace benchmark.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge