How Does Value Distribution in Distributional Reinforcement Learning Help Optimization?
Paper and Code
Sep 29, 2022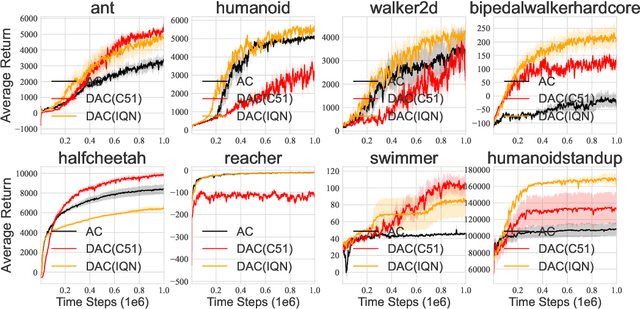
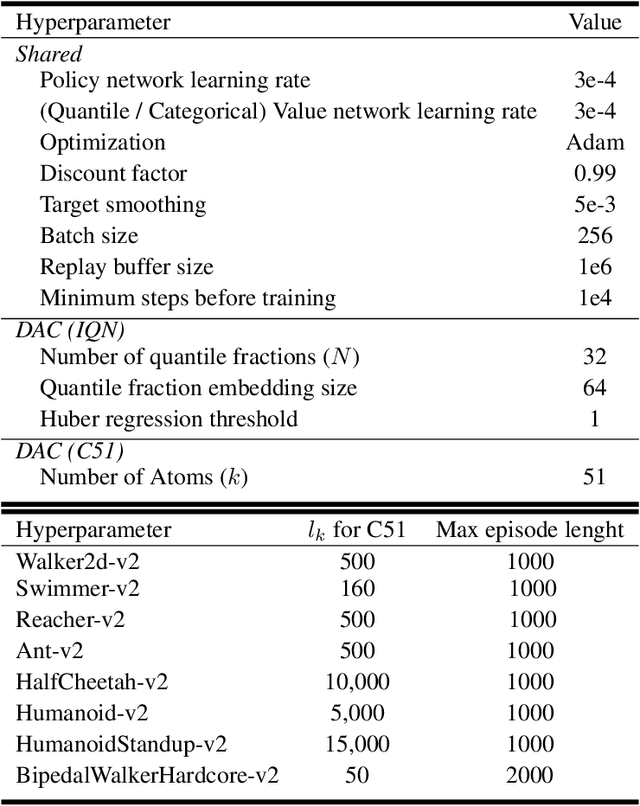
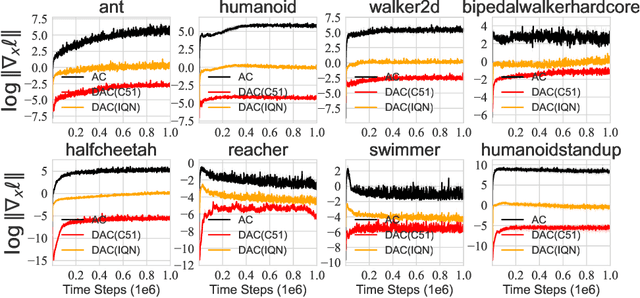
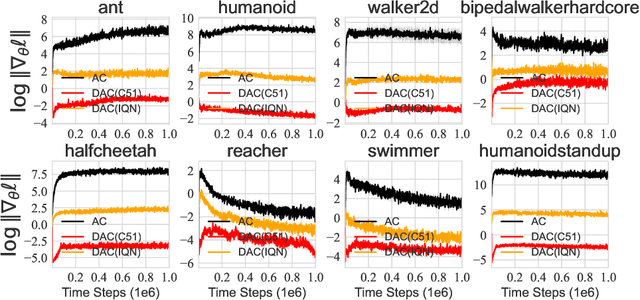
We consider the problem of learning a set of probability distributions from the Bellman dynamics in distributional reinforcement learning~(RL) that learns the whole return distribution compared with only its expectation in classical RL. Despite its success to obtain superior performance, we still have a poor understanding of how the value distribution in distributional RL works. In this study, we analyze the optimization benefits of distributional RL by leverage of additional value distribution information over classical RL in the Neural Fitted Z-Iteration~(Neural FZI) framework. To begin with, we demonstrate that the distribution loss of distributional RL has desirable smoothness characteristics and hence enjoys stable gradients, which is in line with its tendency to promote optimization stability. Furthermore, the acceleration effect of distributional RL is revealed by decomposing the return distribution. It turns out that distributional RL can perform favorably if the value distribution approximation is appropriate, measured by the variance of gradient estimates in each environment for any specific distributional RL algorithm. Rigorous experiments validate the stable optimization behaviors of distributional RL, contributing to its acceleration effects compared to classical RL. The findings of our research illuminate how the value distribution in distributional RL algorithms helps the optimization.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge