HMD-AMP: Protein Language-Powered Hierarchical Multi-label Deep Forest for Annotating Antimicrobial Peptides
Paper and Code
Nov 11, 2021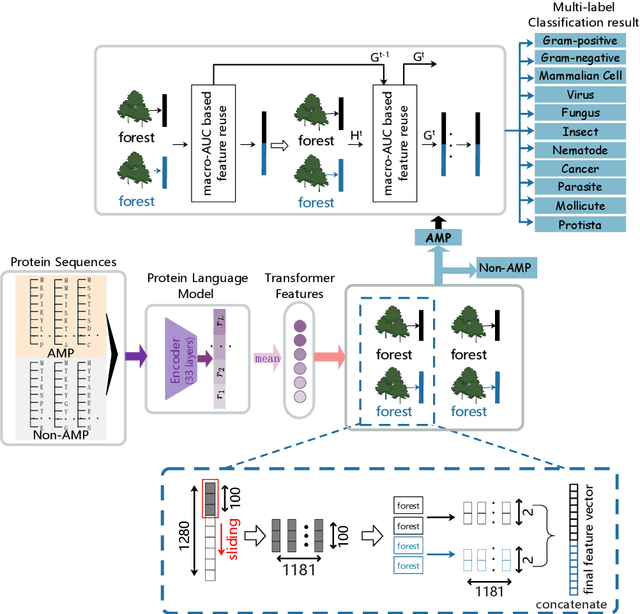
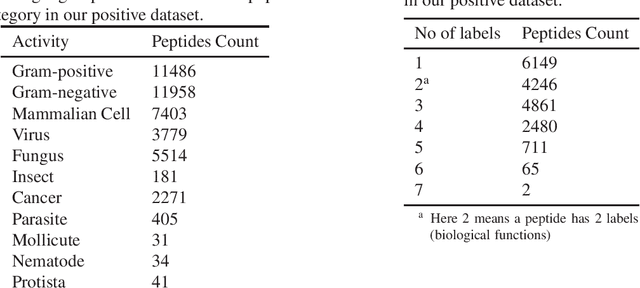
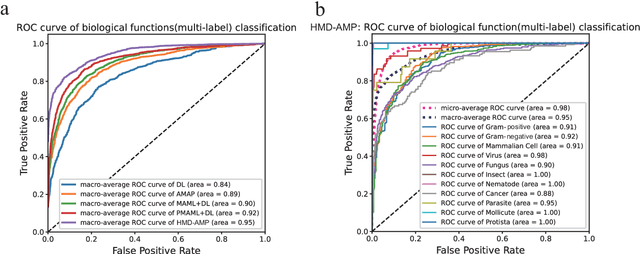
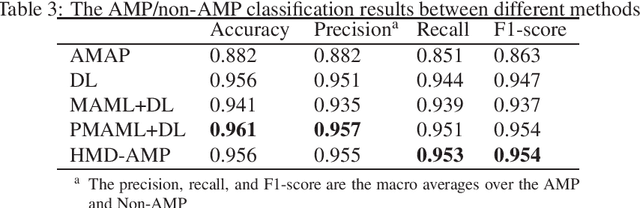
Identifying the targets of an antimicrobial peptide is a fundamental step in studying the innate immune response and combating antibiotic resistance, and more broadly, precision medicine and public health. There have been extensive studies on the statistical and computational approaches to identify (i) whether a peptide is an antimicrobial peptide (AMP) or a non-AMP and (ii) which targets are these sequences effective to (Gram-positive, Gram-negative, etc.). Despite the existing deep learning methods on this problem, most of them are unable to handle the small AMP classes (anti-insect, anti-parasite, etc.). And more importantly, some AMPs can have multiple targets, which the previous methods fail to consider. In this study, we build a diverse and comprehensive multi-label protein sequence database by collecting and cleaning amino acids from various AMP databases. To generate efficient representations and features for the small classes dataset, we take advantage of a protein language model trained on 250 million protein sequences. Based on that, we develop an end-to-end hierarchical multi-label deep forest framework, HMD-AMP, to annotate AMP comprehensively. After identifying an AMP, it further predicts what targets the AMP can effectively kill from eleven available classes. Extensive experiments suggest that our framework outperforms state-of-the-art models in both the binary classification task and the multi-label classification task, especially on the minor classes.The model is robust against reduced features and small perturbations and produces promising results. We believe HMD-AMP contributes to both the future wet-lab investigations of the innate structural properties of different antimicrobial peptides and build promising empirical underpinnings for precise medicine with antibiotics.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge