Hippocampus Segmentation on Epilepsy and Alzheimer's Disease Studies with Multiple Convolutional Neural Networks
Paper and Code
Jan 14, 2020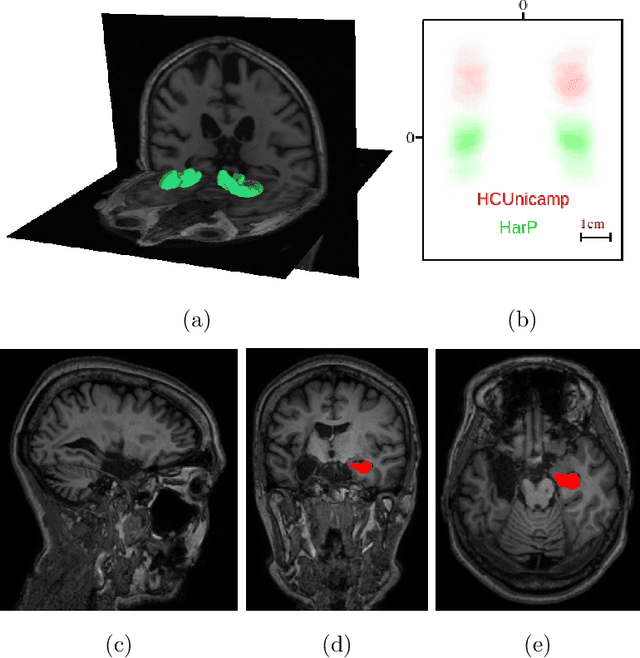

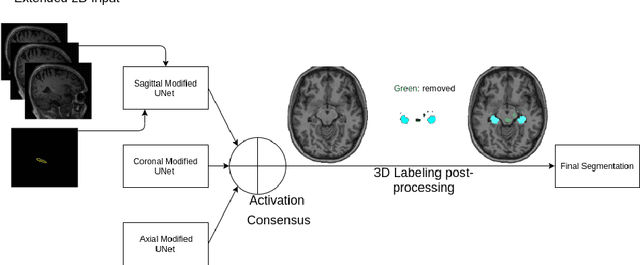
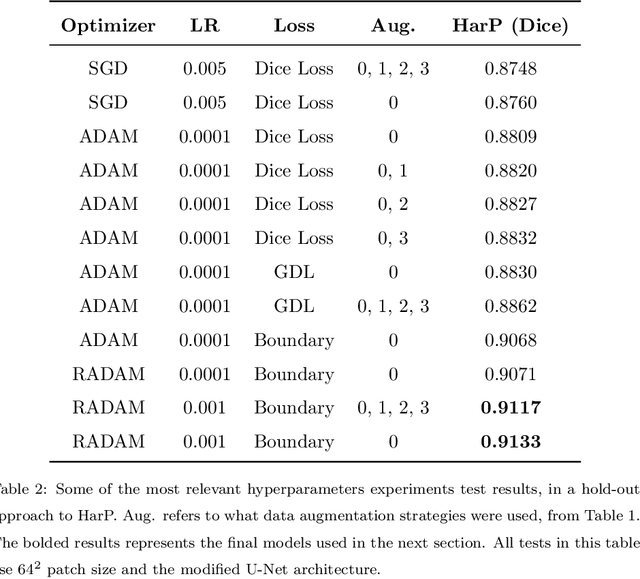
Hippocampus segmentation on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is of key importance for the diagnosis, treatment decision and investigation of neuropsychiatric disorders. Automatic segmentation is a very active research field, with many recent models involving Deep Learning for such task. However, Deep Learning requires a training phase, which can introduce bias from the specific domain of the training dataset. Current state-of-the art methods train their methods on healthy or Alzheimer's disease patients from public datasets. This raises the question whether these methods are capable to recognize the Hippocampus on a very different domain. In this paper we present a state-of-the-art, open source, ready-to-use hippocampus segmentation methodology, using Deep Learning. We analyze this methodology alongside other recent Deep Learning methods, in two domains: the public HarP benchmark and an in-house Epilepsy patients dataset. Our internal dataset differs significantly from Alzheimer's and Healthy subjects scans. Some scans are from patients who have undergone hippocampal resection, due to surgical treatment of Epilepsy. We show that our method surpasses others from the literature in both the Alzheimer's and Epilepsy test datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge