Hierarchical Insights: Exploiting Structural Similarities for Reliable 3D Semantic Segmentation
Paper and Code
Apr 09, 2024
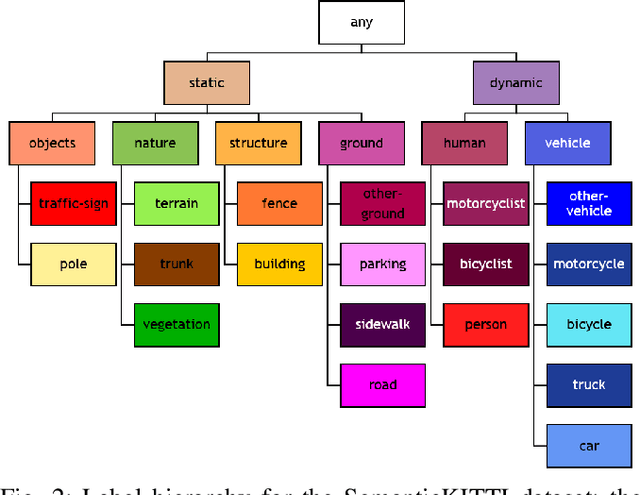

Safety-critical applications like autonomous driving call for robust 3D environment perception algorithms which can withstand highly diverse and ambiguous surroundings. The predictive performance of any classification model strongly depends on the underlying dataset and the prior knowledge conveyed by the annotated labels. While the labels provide a basis for the learning process, they usually fail to represent inherent relations between the classes - representations, which are a natural element of the human perception system. We propose a training strategy which enables a 3D LiDAR semantic segmentation model to learn structural relationships between the different classes through abstraction. We achieve this by implicitly modeling those relationships through a learning rule for hierarchical multi-label classification (HMC). With a detailed analysis we show, how this training strategy not only improves the model's confidence calibration, but also preserves additional information for downstream tasks like fusion, prediction and planning.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge