Guided Learning Convolution System for DCASE 2019 Task 4
Paper and Code
Sep 11, 2019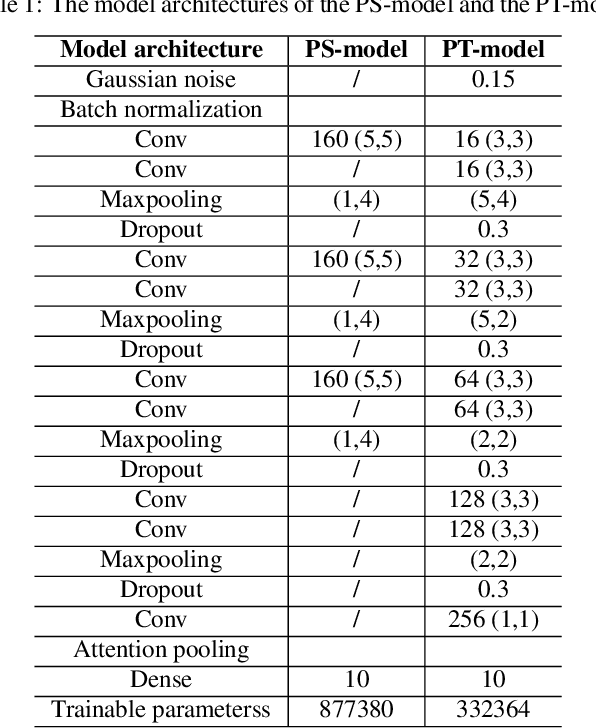


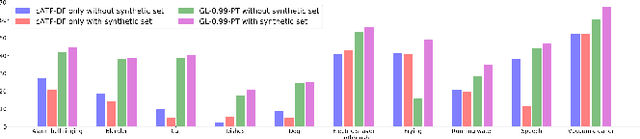
In this paper, we describe in detail the system we submitted to DCASE2019 task 4: sound event detection (SED) in domestic environments. We employ a convolutional neural network (CNN) with an embedding-level attention pooling module to solve it. By considering the interference caused by the co-occurrence of multiple events in the unbalanced dataset, we utilize the disentangled feature to raise the performance of the model. To take advantage of the unlabeled data, we adopt Guided Learning for semi-supervised learning. A group of median filters with adaptive window sizes is utilized in the post-processing of output probabilities of the model. We also analyze the effect of the synthetic data on the performance of the model and finally achieve an event-based F-measure of 45.43% on the validation set and an event-based F-measure of 42.7% on the test set. The system we submitted to the challenge achieves the best performance compared to those of other participates.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge