GSBIQA: Green Saliency-guided Blind Image Quality Assessment Method
Paper and Code
Jul 08, 2024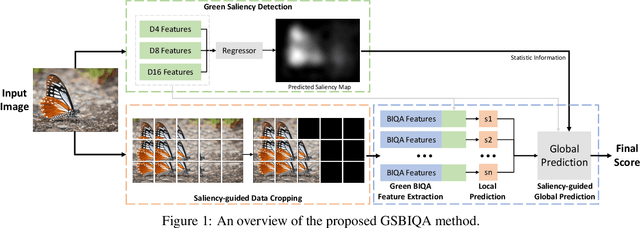
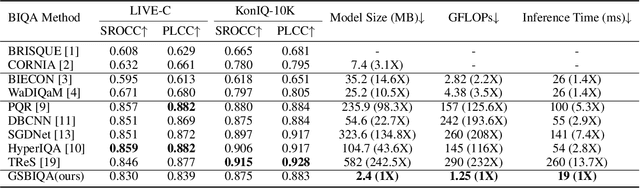
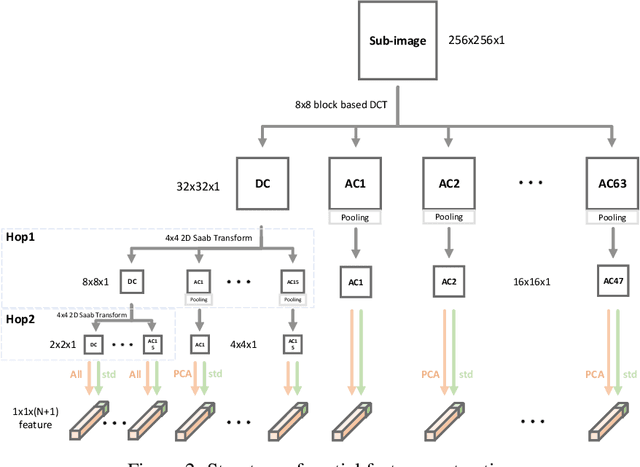

Blind Image Quality Assessment (BIQA) is an essential task that estimates the perceptual quality of images without reference. While many BIQA methods employ deep neural networks (DNNs) and incorporate saliency detectors to enhance performance, their large model sizes limit deployment on resource-constrained devices. To address this challenge, we introduce a novel and non-deep-learning BIQA method with a lightweight saliency detection module, called Green Saliency-guided Blind Image Quality Assessment (GSBIQA). It is characterized by its minimal model size, reduced computational demands, and robust performance. Experimental results show that the performance of GSBIQA is comparable with state-of-the-art DL-based methods with significantly lower resource requirements.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge