Gridless Tomographic SAR Imaging Based on Accelerated Atomic Norm Minimization with Efficiency
Paper and Code
Apr 26, 2022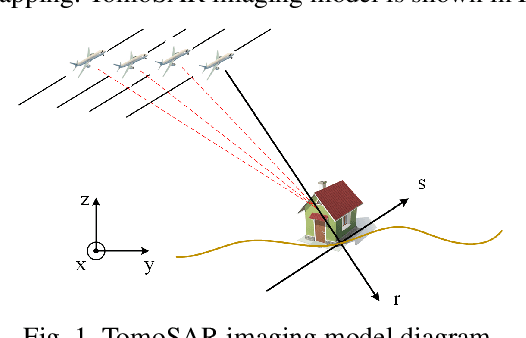
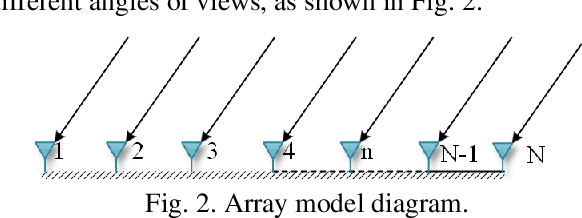

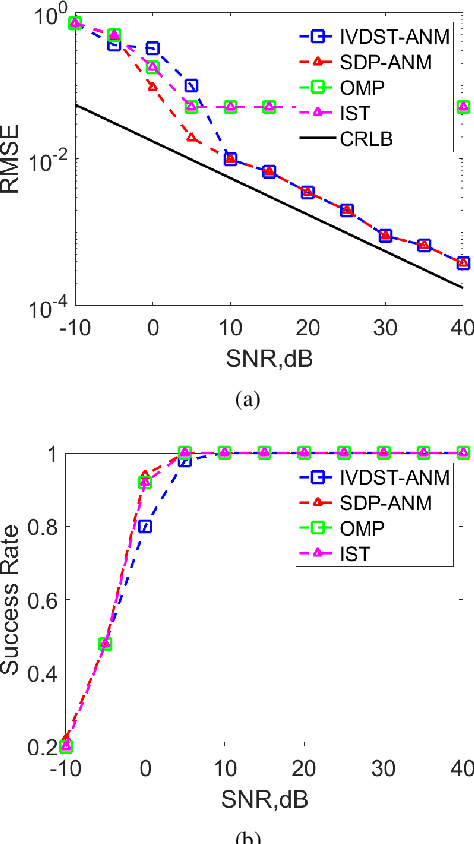
Synthetic aperture radar (SAR) tomography (TomoSAR) enables the reconstruction and three-dimensional (3D) localization of targets based on multiple two-dimensional (2D) observations of the same scene. The resolving along the elevation direction can be treated as a line spectrum estimation problem. However, traditional super-resolution spectrum estimation algorithms require multiple snapshots and uncorrelated targets. Meanwhile, as the most popular TomoSAR imaging method in modern years, compressed sensing (CS) based methods suffer from the gridding mismatch effect which markedly degrades the imaging performance. As a gridless CS approach, atomic norm minimization can avoid the gridding effect but requires enormous computing resources. Addressing the above issues, this paper proposes an improved fast ANM algorithm to TomoSAR elevation focusing by introducing the IVDST-ANM algorithm, which reduces the huge computational complexity of the conventional time-consuming semi-positive definite programming (SDP) by the iterative Vandermonde decomposition and shrinkage-thresholding (IVDST) approach, and retains the benefits of ANM in terms of gridless imaging and single snapshot recovery. We conducted experiments using simulated data to evaluate the performance of the proposed method, and reconstruction results of an urban area from the SARMV3D-Imaging 1.0 dataset are also presented.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge