Greedy Column Subset Selection for Large-scale Data Sets
Paper and Code
Dec 24, 2013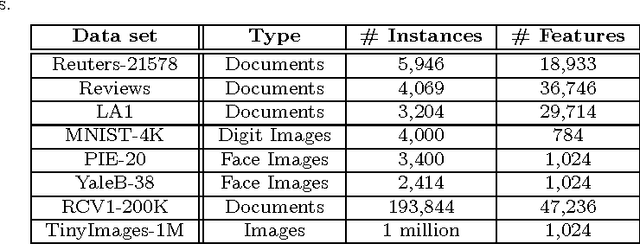
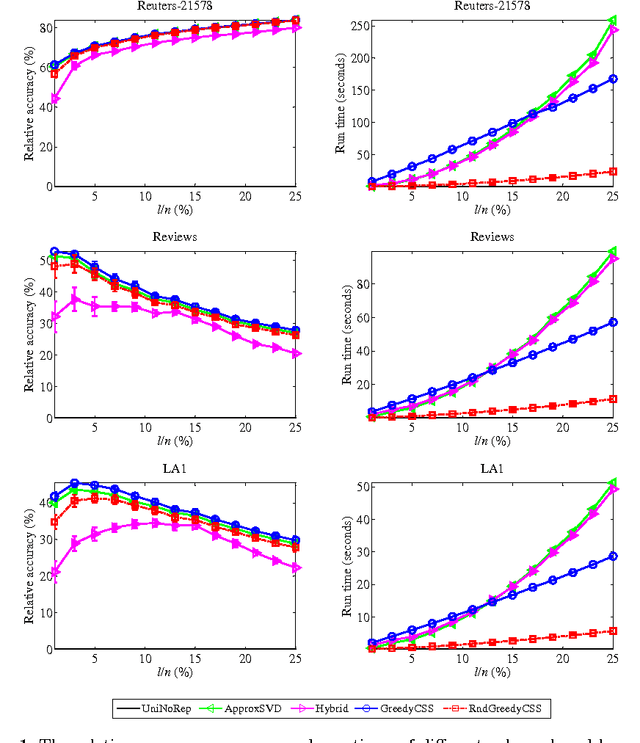
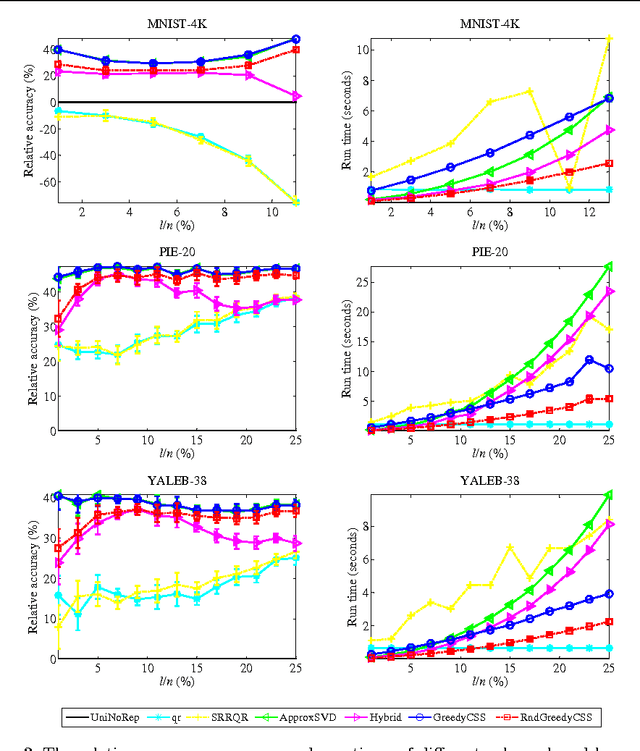
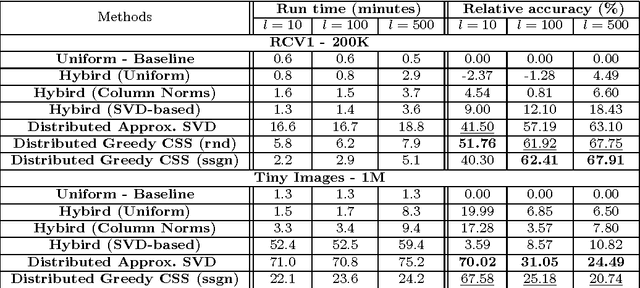
In today's information systems, the availability of massive amounts of data necessitates the development of fast and accurate algorithms to summarize these data and represent them in a succinct format. One crucial problem in big data analytics is the selection of representative instances from large and massively-distributed data, which is formally known as the Column Subset Selection (CSS) problem. The solution to this problem enables data analysts to understand the insights of the data and explore its hidden structure. The selected instances can also be used for data preprocessing tasks such as learning a low-dimensional embedding of the data points or computing a low-rank approximation of the corresponding matrix. This paper presents a fast and accurate greedy algorithm for large-scale column subset selection. The algorithm minimizes an objective function which measures the reconstruction error of the data matrix based on the subset of selected columns. The paper first presents a centralized greedy algorithm for column subset selection which depends on a novel recursive formula for calculating the reconstruction error of the data matrix. The paper then presents a MapReduce algorithm which selects a few representative columns from a matrix whose columns are massively distributed across several commodity machines. The algorithm first learns a concise representation of all columns using random projection, and it then solves a generalized column subset selection problem at each machine in which a subset of columns are selected from the sub-matrix on that machine such that the reconstruction error of the concise representation is minimized. The paper demonstrates the effectiveness and efficiency of the proposed algorithm through an empirical evaluation on benchmark data sets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge