Graph Reasoning with Large Language Models via Pseudo-code Prompting
Paper and Code
Sep 26, 2024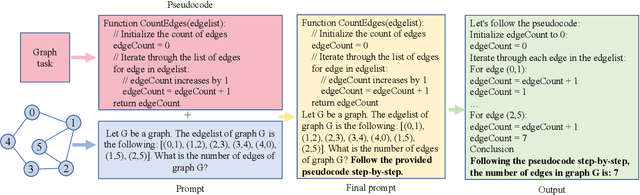
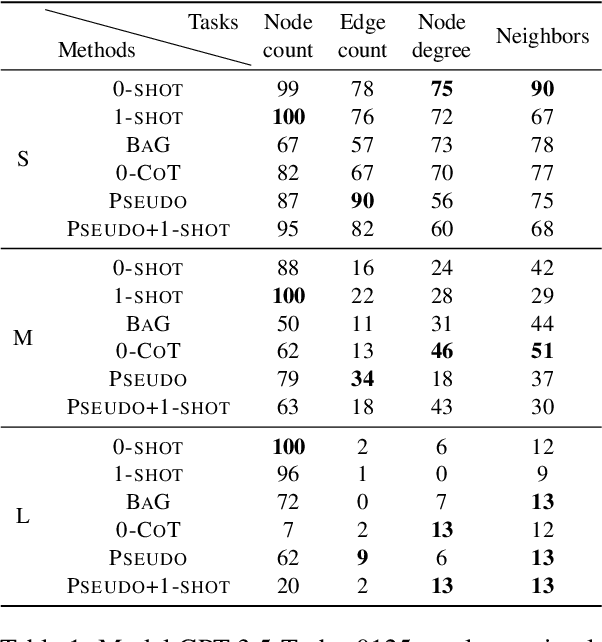
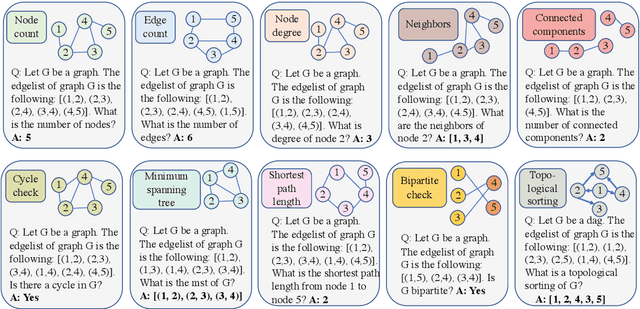
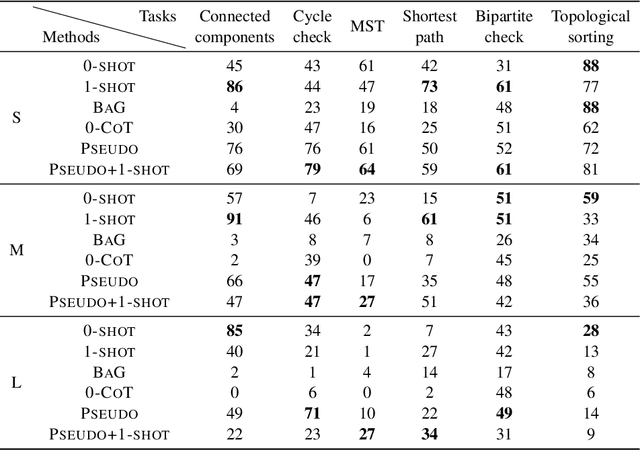
Large language models (LLMs) have recently achieved remarkable success in various reasoning tasks in the field of natural language processing. This success of LLMs has also motivated their use in graph-related tasks. Among others, recent work has explored whether LLMs can solve graph problems such as counting the number of connected components of a graph or computing the shortest path distance between two nodes. Although LLMs possess preliminary graph reasoning abilities, they might still struggle to solve some seemingly simple problems. In this paper, we investigate whether prompting via pseudo-code instructions can improve the performance of LLMs in solving graph problems. Our experiments demonstrate that using pseudo-code instructions generally improves the performance of all considered LLMs. The graphs, pseudo-code prompts, and evaluation code are publicly available.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge