Graph Neural Network to Dilute Outliers for Refactoring Monolith Application
Paper and Code
Feb 07, 2021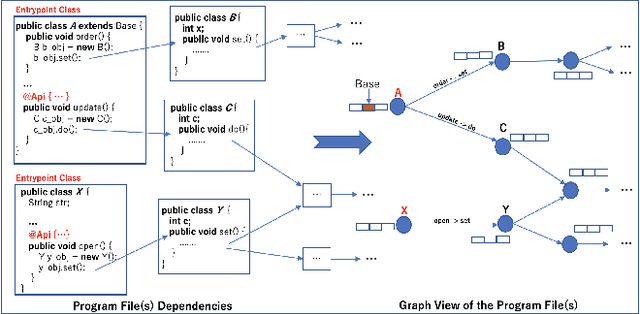
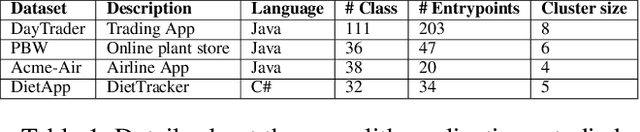
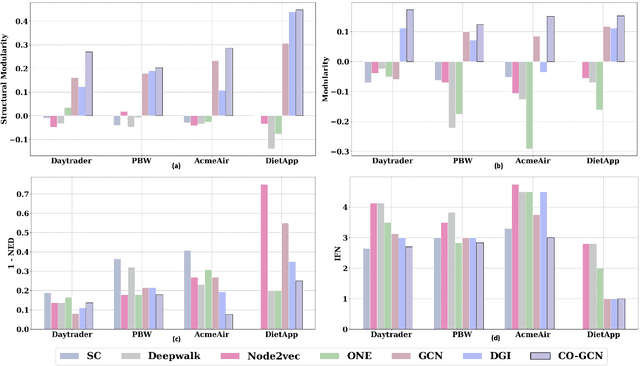
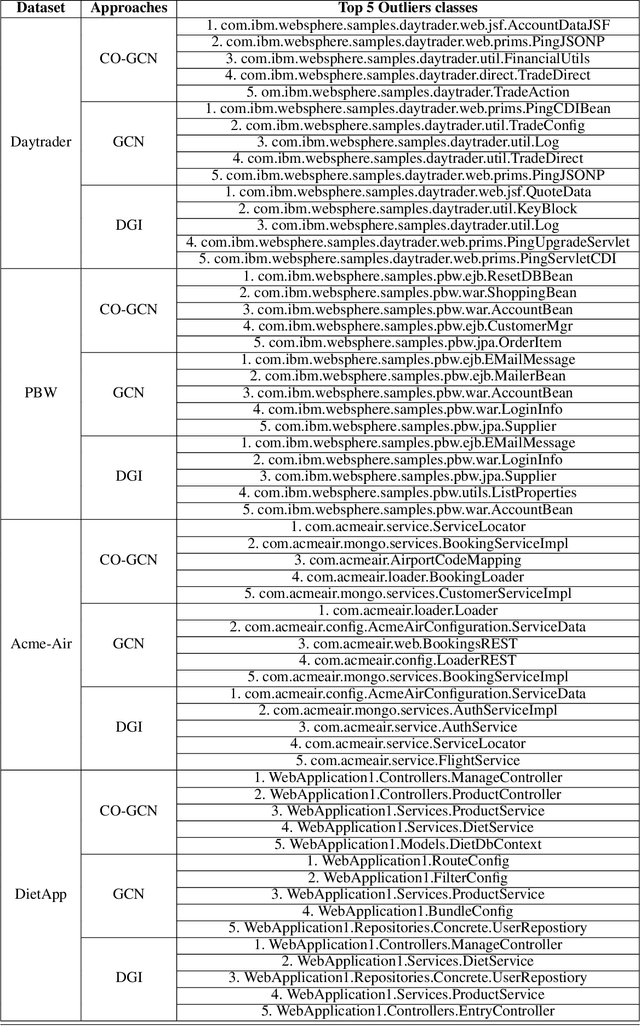
Microservices are becoming the defacto design choice for software architecture. It involves partitioning the software components into finer modules such that the development can happen independently. It also provides natural benefits when deployed on the cloud since resources can be allocated dynamically to necessary components based on demand. Therefore, enterprises as part of their journey to cloud, are increasingly looking to refactor their monolith application into one or more candidate microservices; wherein each service contains a group of software entities (e.g., classes) that are responsible for a common functionality. Graphs are a natural choice to represent a software system. Each software entity can be represented as nodes and its dependencies with other entities as links. Therefore, this problem of refactoring can be viewed as a graph based clustering task. In this work, we propose a novel method to adapt the recent advancements in graph neural networks in the context of code to better understand the software and apply them in the clustering task. In that process, we also identify the outliers in the graph which can be directly mapped to top refactor candidates in the software. Our solution is able to improve state-of-the-art performance compared to works from both software engineering and existing graph representation based techniques.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge