Graph Meets LLM: A Novel Approach to Collaborative Filtering for Robust Conversational Understanding
Paper and Code
May 23, 2023
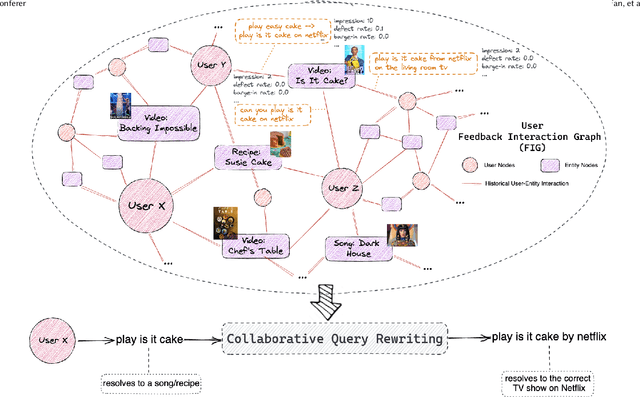
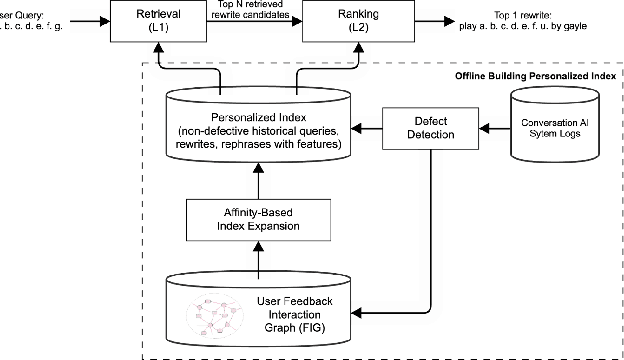
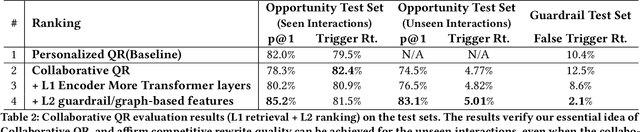
Conversational AI systems (e.g. Alexa, Siri, Google Assistant, etc.) need to understand queries with defects to ensure robust conversational understanding and reduce user frictions. The defective queries are often induced by user ambiguities and mistakes, or errors in the automatic speech recognition (ASR) and natural language understanding (NLU). Personalized query rewriting (personalized QR) targets reducing defects in the torso and tail user query traffic, and it typically relies on an index of past successful user interactions with the conversational AI. This paper presents our "Collaborative Query Rewriting" approach that focuses on rewriting novel user interactions unseen in the user history. This approach builds a "user Feedback Interaction Graph" (FIG) consisting of historical user-entity interactions, and leverages multi-hop customer affinity to enrich each user's index (i.e. the Collaborative User Index) that would help cover future unseen defective queries. To counteract the precision degradation from the enlarged index, we introduced additional transformer layers to the L1 retrieval model and added multi-hop affinity and guardrail features to the L2 re-ranking model. Given the production constraints of storage cost and runtime retrieval latency, managing the size of the Collaborative User Index is important. As the user index can be pre-computed, we explored using a Large Language Model (LLM) for multi-hop customer affinity retrieval on the Video/Music domains. In particular, this paper looked into the Dolly-V2 7B model. Given limited user index size, We found the user index derived from fine-tuned Dolly-V2 generation significantly enhanced coverage of unseen user interactions. Consequently, this boosted QR performance on unseen user interactions compared to the graph traversal based user index.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge