GraNet: Global Relation-aware Attentional Network for ALS Point Cloud Classification
Paper and Code
Dec 24, 2020
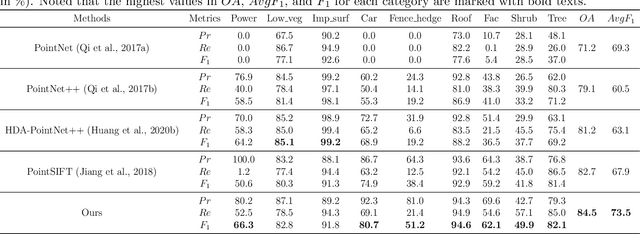
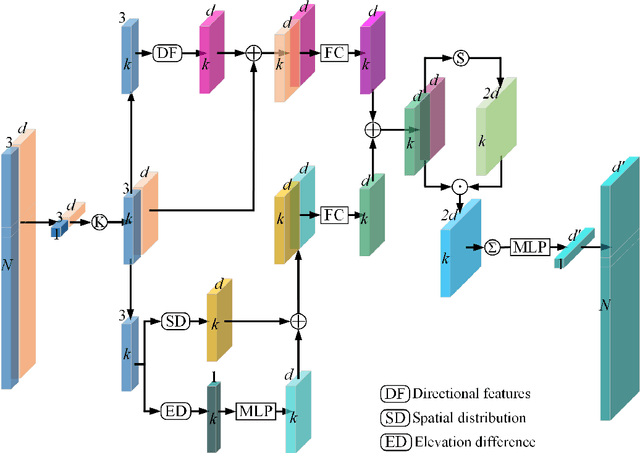
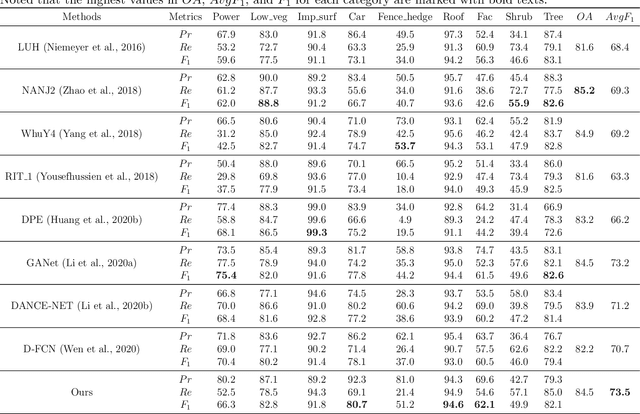
In this work, we propose a novel neural network focusing on semantic labeling of ALS point clouds, which investigates the importance of long-range spatial and channel-wise relations and is termed as global relation-aware attentional network (GraNet). GraNet first learns local geometric description and local dependencies using a local spatial discrepancy attention convolution module (LoSDA). In LoSDA, the orientation information, spatial distribution, and elevation differences are fully considered by stacking several local spatial geometric learning modules and the local dependencies are embedded by using an attention pooling module. Then, a global relation-aware attention module (GRA), consisting of a spatial relation-aware attention module (SRA) and a channel relation aware attention module (CRA), are investigated to further learn the global spatial and channel-wise relationship between any spatial positions and feature vectors. The aforementioned two important modules are embedded in the multi-scale network architecture to further consider scale changes in large urban areas. We conducted comprehensive experiments on two ALS point cloud datasets to evaluate the performance of our proposed framework. The results show that our method can achieve higher classification accuracy compared with other commonly used advanced classification methods. The overall accuracy (OA) of our method on the ISPRS benchmark dataset can be improved to 84.5% to classify nine semantic classes, with an average F1 measure (AvgF1) of 73.5%. In detail, we have following F1 values for each object class: powerlines: 66.3%, low vegetation: 82.8%, impervious surface: 91.8%, car: 80.7%, fence: 51.2%, roof: 94.6%, facades: 62.1%, shrub: 49.9%, trees: 82.1%. Besides, experiments were conducted using a new ALS point cloud dataset covering highly dense urban areas.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge