Goal-directed Planning and Goal Understanding by Active Inference: Evaluation Through Simulated and Physical Robot Experiments
Paper and Code
Feb 21, 2022
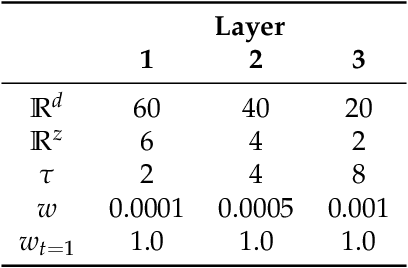
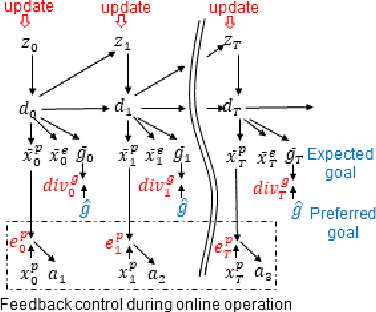

We show that goal-directed action planning and generation in a teleological framework can be formulated using the free energy principle. The proposed model, which is built on a variational recurrent neural network model, is characterized by three essential features. These are that (1) goals can be specified for both static sensory states, e.g., for goal images to be reached and dynamic processes, e.g., for moving around an object, (2) the model can not only generate goal-directed action plans, but can also understand goals by sensory observation, and (3) the model generates future action plans for given goals based on the best estimate of the current state, inferred using past sensory observations. The proposed model is evaluated by conducting experiments on a simulated mobile agent as well as on a real humanoid robot performing object manipulation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge