gl2vec: Learning Feature Representation Using Graphlets for Directed Networks
Paper and Code
Dec 13, 2018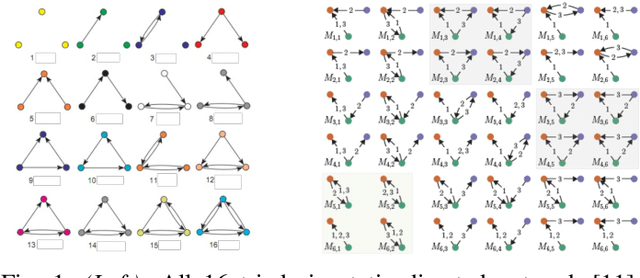
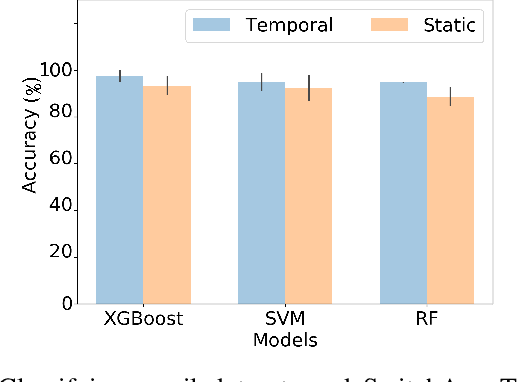
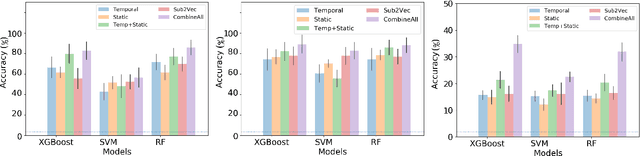
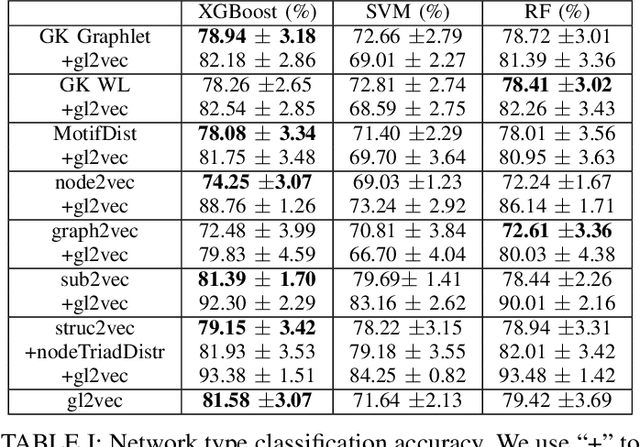
Learning network representations has a variety of applications, such as network classification. Most existing work in this area focuses on static undirected networks and do not account for presence of directed edges or temporarily changes. Furthermore, most work focuses on node representations that do poorly on tasks like network classification. In this paper, we propose a novel, flexible and scalable network embedding methodology, \emph{gl2vec}, for network classification in both static and temporal directed networks. \emph{gl2vec} constructs vectors for feature representation using static or temporal network graphlet distributions and a null model for comparing them against random graphs. We argue that \emph{gl2vec} can be used to classify and compare networks of varying sizes and time period with high accuracy. We demonstrate the efficacy and usability of \emph{gl2vec} over existing state-of-the-art methods on network classification tasks such as network type classification and subgraph identification in several real-world static and temporal directed networks. Experimental results further show that \emph{gl2vec}, concatenated with a wide range of state-of-the-art methods, improves classification accuracy by up to $10\%$ in real-world applications such as detecting departments for subgraphs in an email network or identifying mobile users given their app switching behaviors represented as static or temporal directed networks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge