GENESIM: genetic extraction of a single, interpretable model
Paper and Code
Nov 17, 2016

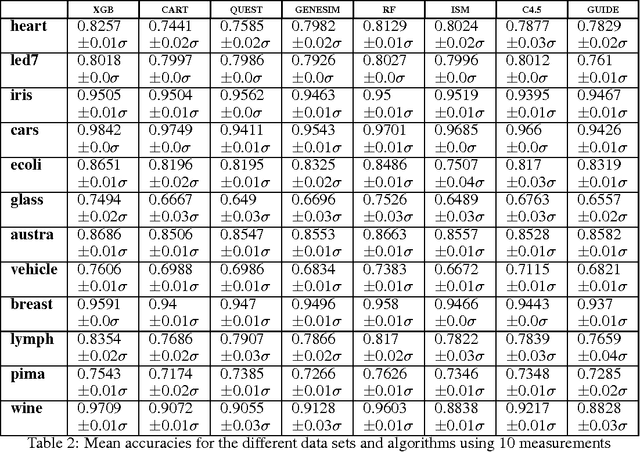
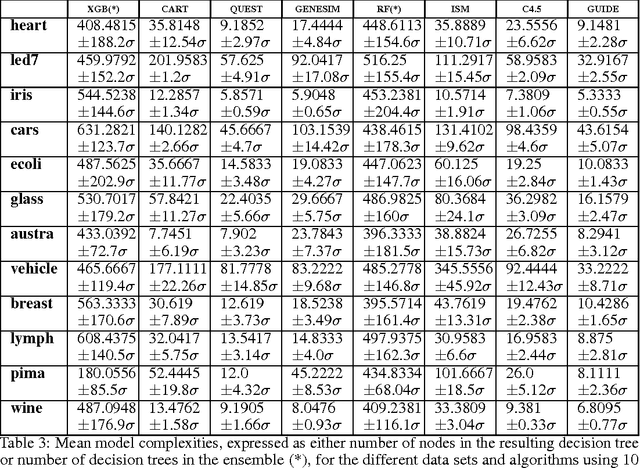
Models obtained by decision tree induction techniques excel in being interpretable.However, they can be prone to overfitting, which results in a low predictive performance. Ensemble techniques are able to achieve a higher accuracy. However, this comes at a cost of losing interpretability of the resulting model. This makes ensemble techniques impractical in applications where decision support, instead of decision making, is crucial. To bridge this gap, we present the GENESIM algorithm that transforms an ensemble of decision trees to a single decision tree with an enhanced predictive performance by using a genetic algorithm. We compared GENESIM to prevalent decision tree induction and ensemble techniques using twelve publicly available data sets. The results show that GENESIM achieves a better predictive performance on most of these data sets than decision tree induction techniques and a predictive performance in the same order of magnitude as the ensemble techniques. Moreover, the resulting model of GENESIM has a very low complexity, making it very interpretable, in contrast to ensemble techniques.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge