Generative Adversarial Nets from a Density Ratio Estimation Perspective
Paper and Code
Nov 09, 2016

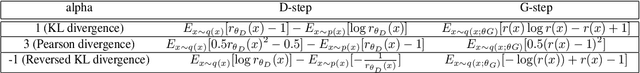
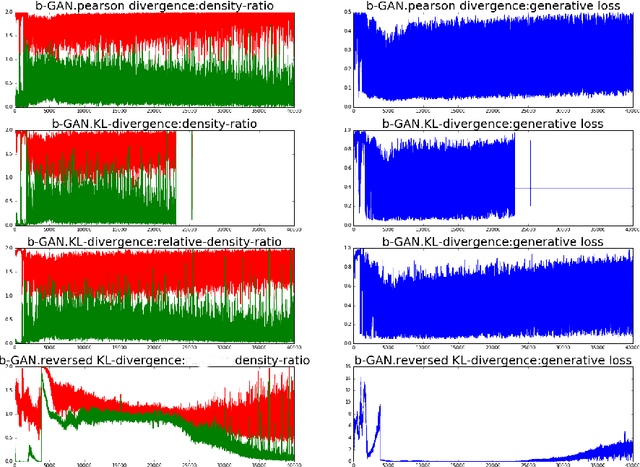
Generative adversarial networks (GANs) are successful deep generative models. GANs are based on a two-player minimax game. However, the objective function derived in the original motivation is changed to obtain stronger gradients when learning the generator. We propose a novel algorithm that repeats the density ratio estimation and f-divergence minimization. Our algorithm offers a new perspective toward the understanding of GANs and is able to make use of multiple viewpoints obtained in the research of density ratio estimation, e.g. what divergence is stable and relative density ratio is useful.
* Add contents especially theoretical things for ICLR 2017
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge