Generalized Classification of Satellite Image Time Series with Thermal Positional Encoding
Paper and Code
Mar 17, 2022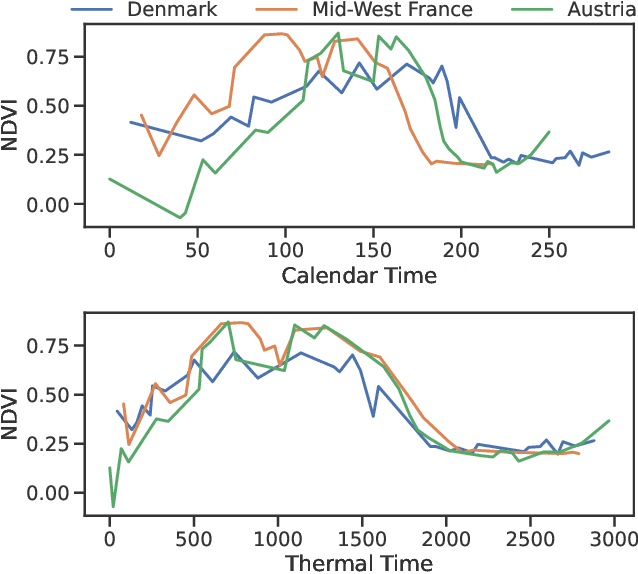
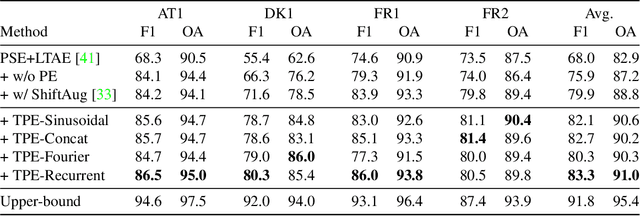
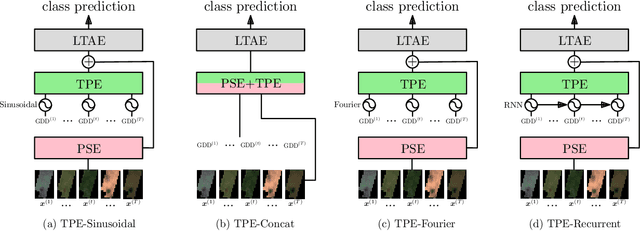
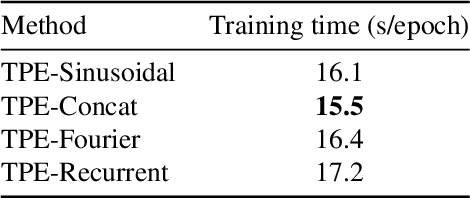
Large-scale crop type classification is a task at the core of remote sensing efforts with applications of both economic and ecological importance. Current state-of-the-art deep learning methods are based on self-attention and use satellite image time series (SITS) to discriminate crop types based on their unique growth patterns. However, existing methods generalize poorly to regions not seen during training mainly due to not being robust to temporal shifts of the growing season caused by variations in climate. To this end, we propose Thermal Positional Encoding (TPE) for attention-based crop classifiers. Unlike previous positional encoding based on calendar time (e.g. day-of-year), TPE is based on thermal time, which is obtained by accumulating daily average temperatures over the growing season. Since crop growth is directly related to thermal time, but not calendar time, TPE addresses the temporal shifts between different regions to improve generalization. We propose multiple TPE strategies, including learnable methods, to further improve results compared to the common fixed positional encodings. We demonstrate our approach on a crop classification task across four different European regions, where we obtain state-of-the-art generalization results.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge