Generalizability Analysis of Graph-based Trajectory Predictor with Vectorized Representation
Paper and Code
Aug 06, 2022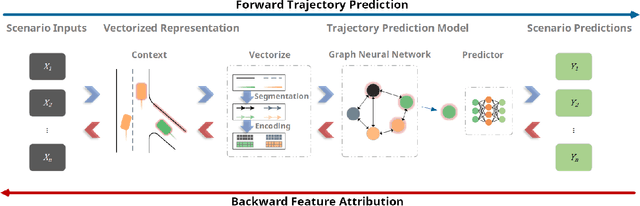
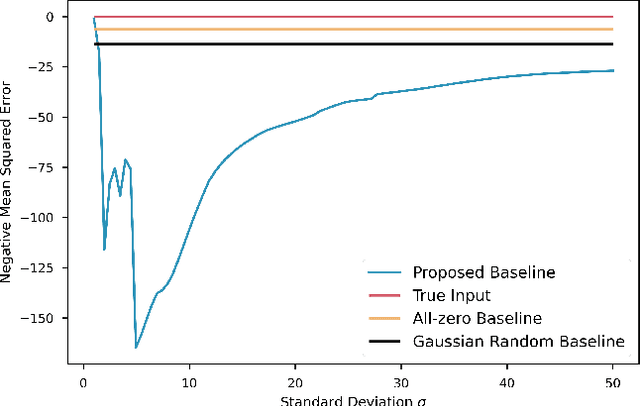
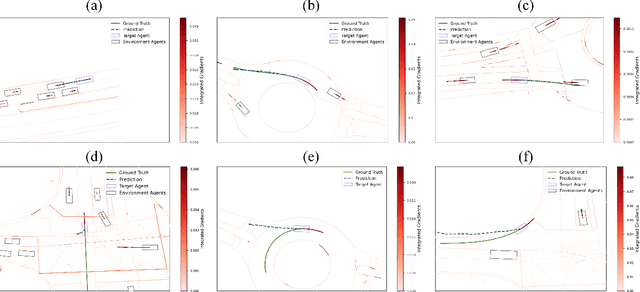
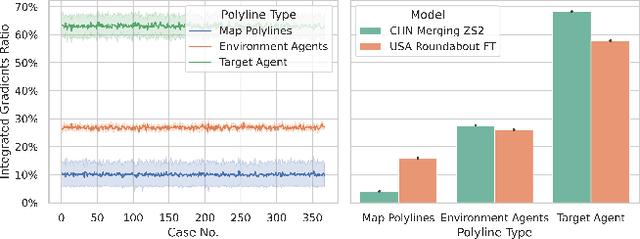
Trajectory prediction is one of the essential tasks for autonomous vehicles. Recent progress in machine learning gave birth to a series of advanced trajectory prediction algorithms. Lately, the effectiveness of using graph neural networks (GNNs) with vectorized representations for trajectory prediction has been demonstrated by many researchers. Nonetheless, these algorithms either pay little attention to models' generalizability across various scenarios or simply assume training and test data follow similar statistics. In fact, when test scenarios are unseen or Out-of-Distribution (OOD), the resulting train-test domain shift usually leads to significant degradation in prediction performance, which will impact downstream modules and eventually lead to severe accidents. Therefore, it is of great importance to thoroughly investigate the prediction models in terms of their generalizability, which can not only help identify their weaknesses but also provide insights on how to improve these models. This paper proposes a generalizability analysis framework using feature attribution methods to help interpret black-box models. For the case study, we provide an in-depth generalizability analysis of one of the state-of-the-art graph-based trajectory predictors that utilize vectorized representation. Results show significant performance degradation due to domain shift, and feature attribution provides insights to identify potential causes of these problems. Finally, we conclude the common prediction challenges and how weighting biases induced by the training process can deteriorate the accuracy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge