Generalised $f$-Mean Aggregation for Graph Neural Networks
Paper and Code
Jun 24, 2023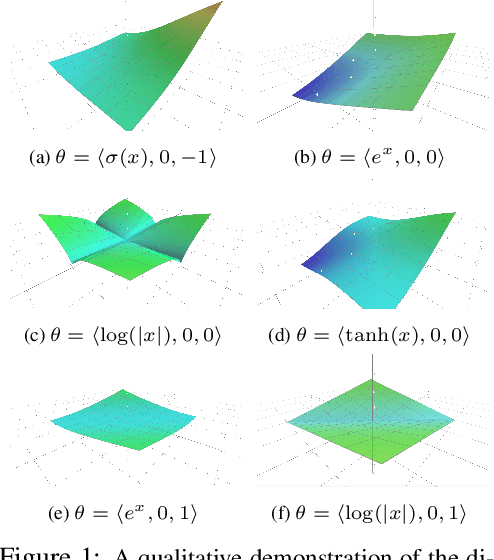
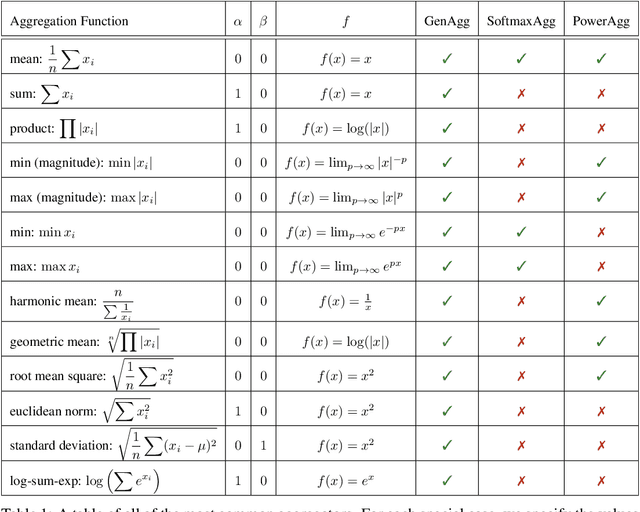
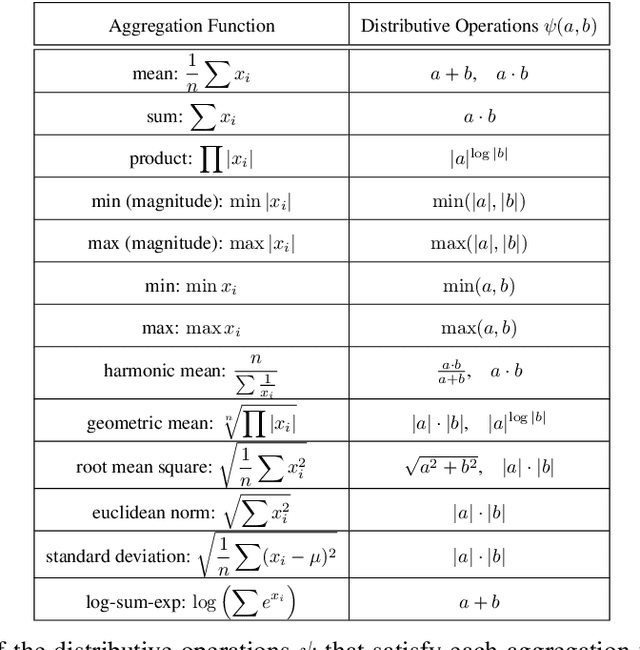
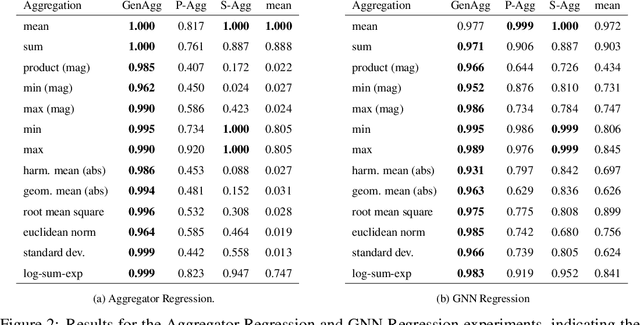
Graph Neural Network (GNN) architectures are defined by their implementations of update and aggregation modules. While many works focus on new ways to parametrise the update modules, the aggregation modules receive comparatively little attention. Because it is difficult to parametrise aggregation functions, currently most methods select a "standard aggregator" such as $\mathrm{mean}$, $\mathrm{sum}$, or $\mathrm{max}$. While this selection is often made without any reasoning, it has been shown that the choice in aggregator has a significant impact on performance, and the best choice in aggregator is problem-dependent. Since aggregation is a lossy operation, it is crucial to select the most appropriate aggregator in order to minimise information loss. In this paper, we present GenAgg, a generalised aggregation operator, which parametrises a function space that includes all standard aggregators. In our experiments, we show that GenAgg is able to represent the standard aggregators with much higher accuracy than baseline methods. We also show that using GenAgg as a drop-in replacement for an existing aggregator in a GNN often leads to a significant boost in performance across various tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge