General Methods for Evaluating Collision Probability of Different Types of Theta-phi Positioners
Paper and Code
Sep 11, 2024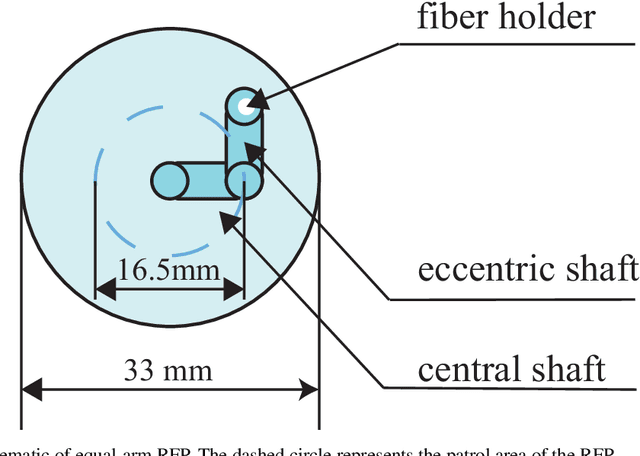

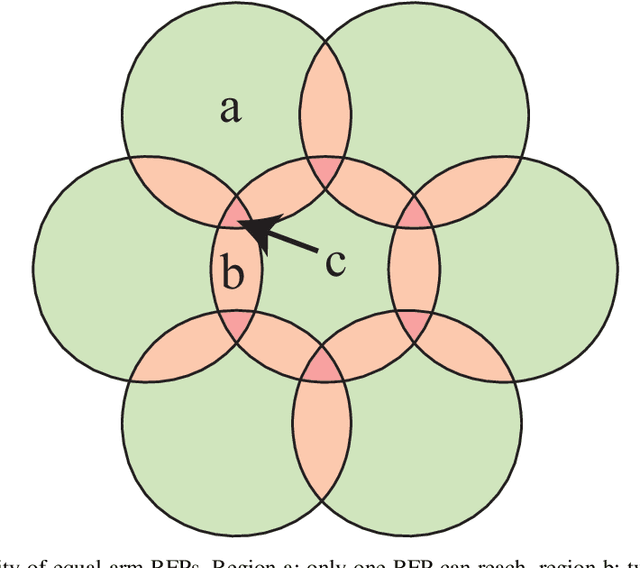
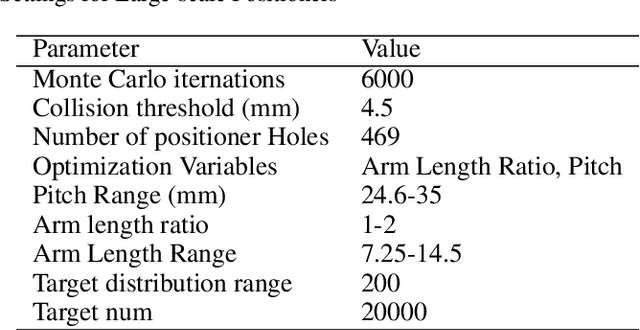
In many modern astronomical facilities, multi-object telescopes are crucial instruments. Most of these telescopes have thousands of robotic fiber positioners(RFPs) installed on their focal plane, sharing an overlapping workspace. Collisions between RFPs during their movement can result in some targets becoming unreachable and cause structural damage. Therefore, it is necessary to reasonably assess and evaluate the collision probability of the RFPs. In this study, we propose a mathematical models of collision probability and validate its results using Monte Carlo simulations. In addition, a new collision calculation method is proposed for faster calculation(nearly 0.15% of original time). Simulation experiments have verified that our method can evaluate the collision probability between RFPs with both equal and unequal arm lengths. Additionally, we found that adopting a target distribution based on a Poisson distribution can reduce the collision probability by approximately 2.6% on average.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge