From Style to Facts: Mapping the Boundaries of Knowledge Injection with Finetuning
Paper and Code
Mar 07, 2025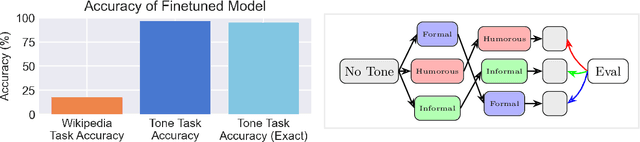
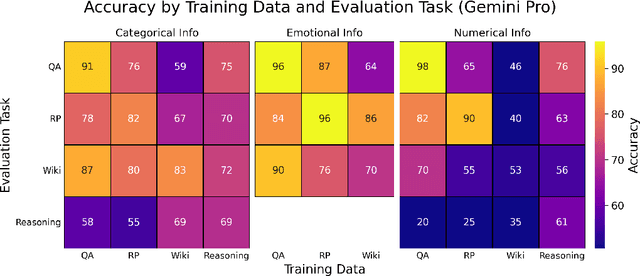
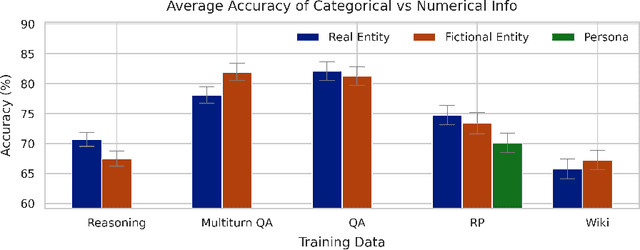
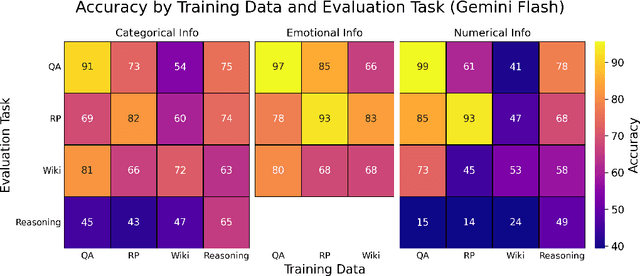
Finetuning provides a scalable and cost-effective means of customizing language models for specific tasks or response styles, with greater reliability than prompting or in-context learning. In contrast, the conventional wisdom is that injecting knowledge via finetuning results in brittle performance and poor generalization. We argue that the dichotomy of "task customization" (e.g., instruction tuning) and "knowledge injection" (e.g., teaching new facts) is a distinction without a difference. We instead identify concrete factors that explain the heterogeneous effectiveness observed with finetuning. To this end, we conduct a large-scale experimental study of finetuning the frontier Gemini v1.5 model family on a spectrum of datasets that are artificially engineered to interpolate between the strengths and failure modes of finetuning. Our findings indicate that question-answer training data formats provide much stronger knowledge generalization than document/article-style training data, numerical information can be harder for finetuning to retain than categorical information, and models struggle to apply finetuned knowledge during multi-step reasoning even when trained on similar examples -- all factors that render "knowledge injection" to be especially difficult, even after controlling for considerations like data augmentation and information volume. On the other hand, our findings also indicate that it is not fundamentally more difficult to finetune information about a real-world event than information about what a model's writing style should be.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge