Frequency Matters: Explaining Biases of Face Recognition in the Frequency Domain
Paper and Code
Jan 28, 2025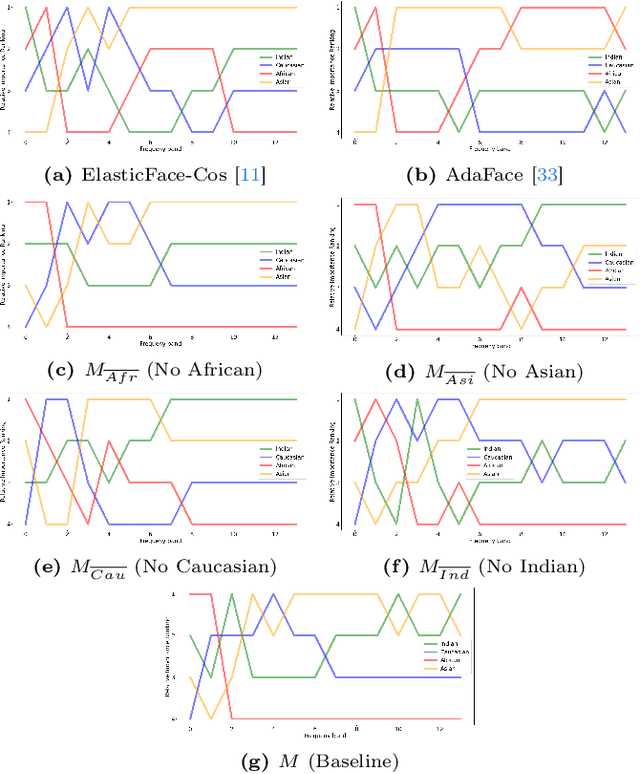
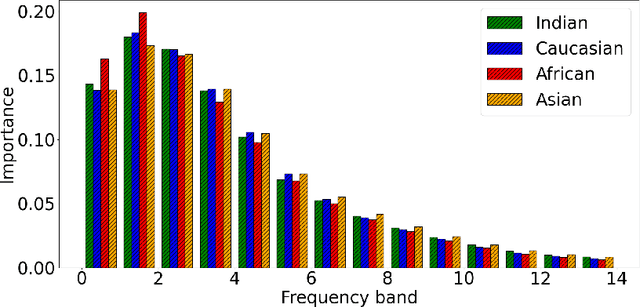
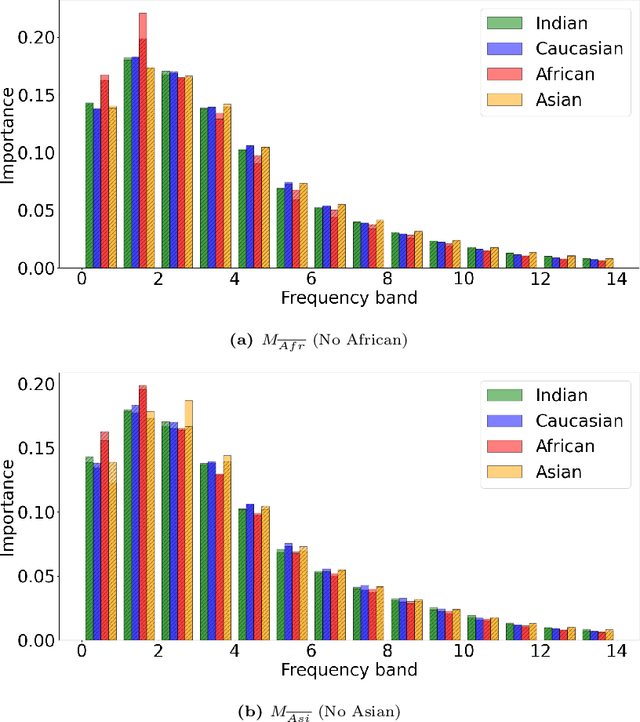
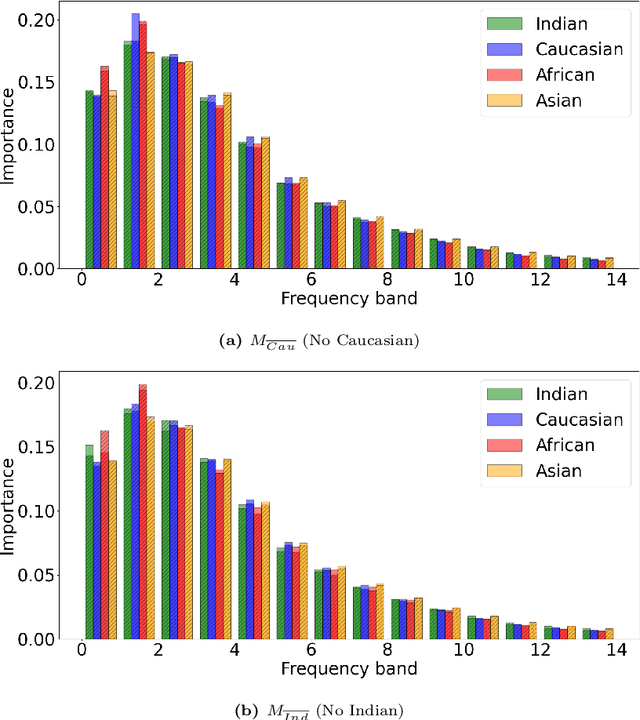
Face recognition (FR) models are vulnerable to performance variations across demographic groups. The causes for these performance differences are unclear due to the highly complex deep learning-based structure of face recognition models. Several works aimed at exploring possible roots of gender and ethnicity bias, identifying semantic reasons such as hairstyle, make-up, or facial hair as possible sources. Motivated by recent discoveries of the importance of frequency patterns in convolutional neural networks, we explain bias in face recognition using state-of-the-art frequency-based explanations. Our extensive results show that different frequencies are important to FR models depending on the ethnicity of the samples.
* Accepted at xAI4Biometrics at ECCV 2024
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge