Free energy-based reinforcement learning using a quantum processor
Paper and Code
May 29, 2017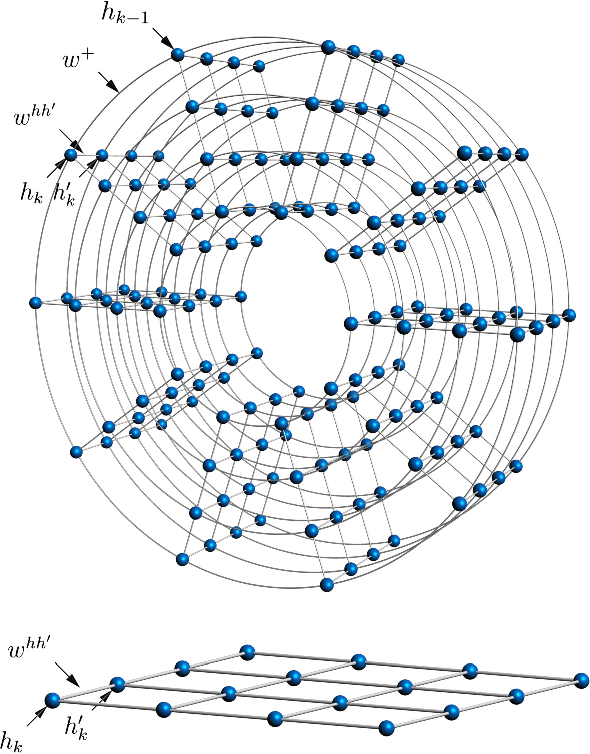
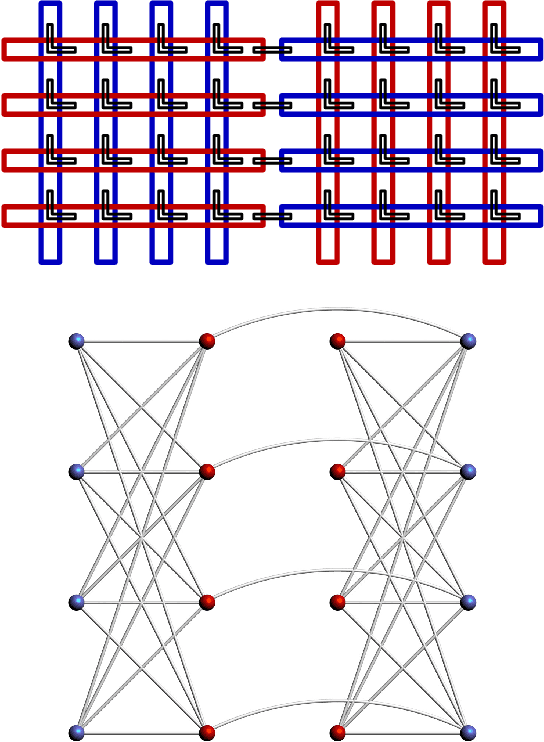
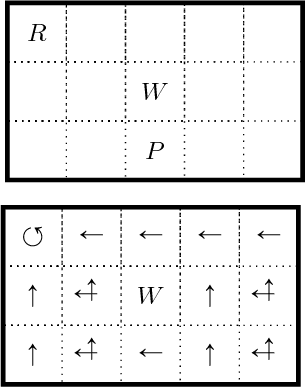
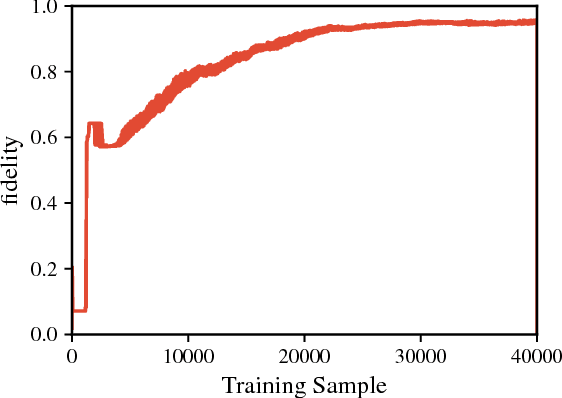
Recent theoretical and experimental results suggest the possibility of using current and near-future quantum hardware in challenging sampling tasks. In this paper, we introduce free energy-based reinforcement learning (FERL) as an application of quantum hardware. We propose a method for processing a quantum annealer's measured qubit spin configurations in approximating the free energy of a quantum Boltzmann machine (QBM). We then apply this method to perform reinforcement learning on the grid-world problem using the D-Wave 2000Q quantum annealer. The experimental results show that our technique is a promising method for harnessing the power of quantum sampling in reinforcement learning tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge