Four-dimensional Gait Surfaces for A Tilt-rotor -- Two Color Map Theorem
Paper and Code
Apr 04, 2022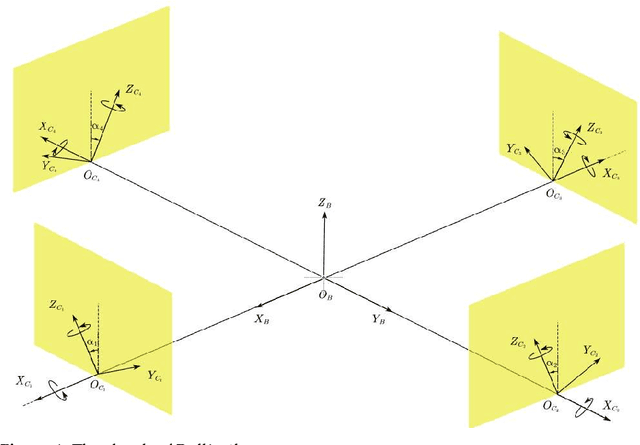
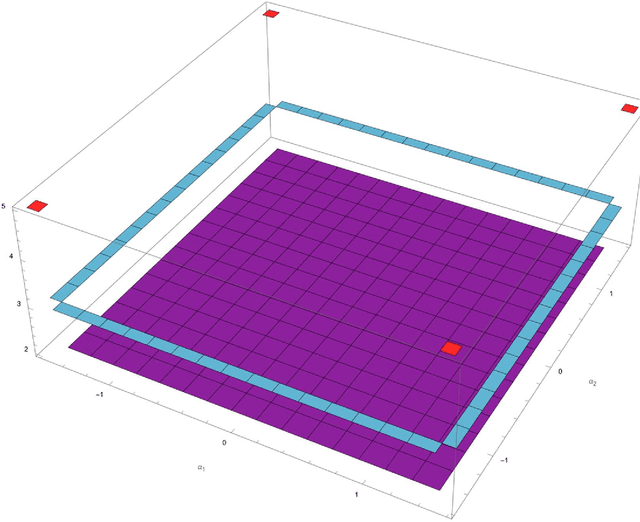
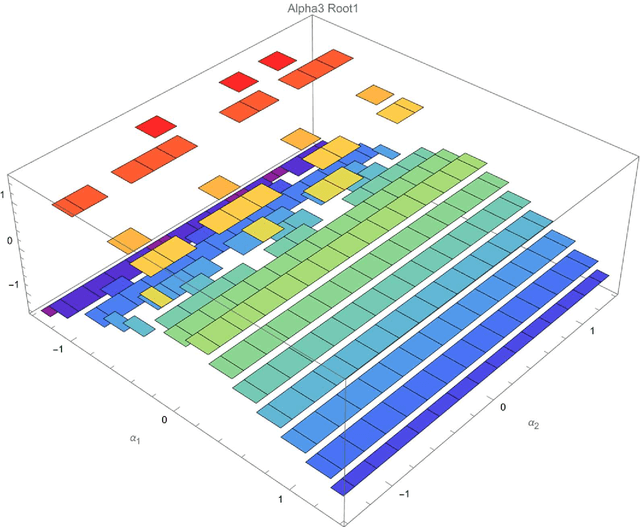
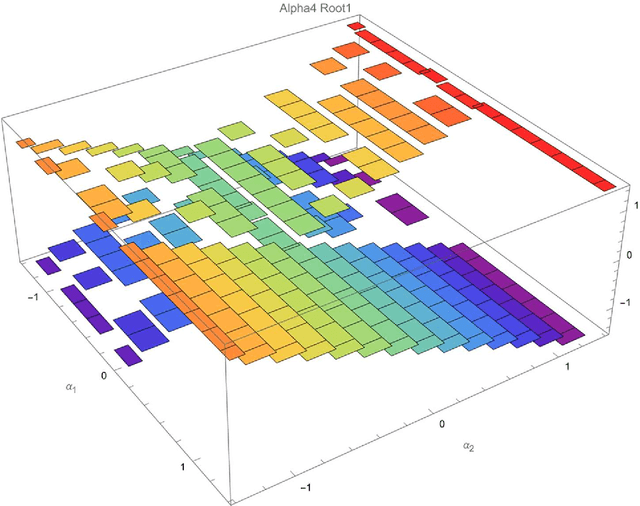
This article presents the four-dimensional surfaces which instruct the gait plan for a tilt-rotor. The previous gaits analyzed in the tilt-rotor research are inspired by animals; no theoretical base backs the robustness of these gaits. This research deduces the gaits by diminishing the effect of the attitude of the tilt-rotor for the first time. Four-dimensional gait surfaces are subsequently found, on which the gaits are expected to be robust to the attitude. These surfaces provide the region where the gait is suggested to be planned. However, a discontinuous region may hinder the gait plan process while utilizing the proposal gait surfaces. A Two Color Map Theorem is then established to guarantee the continuity of each gait designed. The robustness of the typical gaits obeying the Two Color Map Theorem and on the gait surface is demonstrated by comparing the singular curve in attitude with the gaits not on the gait surface. The result shows that the acceptable attitudes enlarge for the gaits on the gait surface.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge