Formal Specification and Analysis of Autonomous Systems under Partial Compliance
Paper and Code
Jul 22, 2016
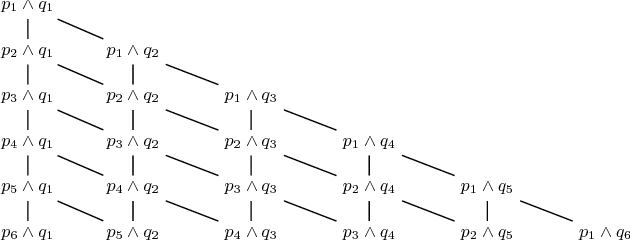
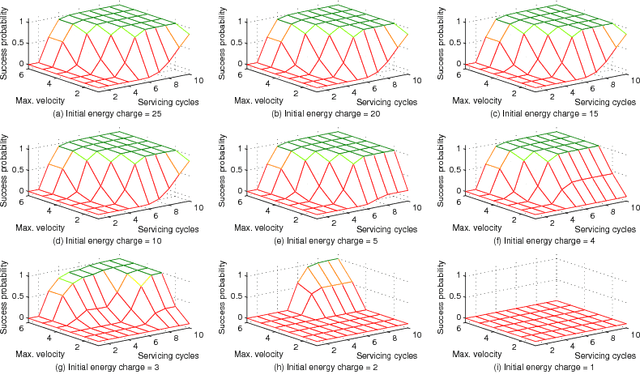
The widespread adoption of autonomous systems depends on providing guarantees of safety and functional correctness, at both design time and runtime. Information about the extent to which functional requirements can be met in combination with non-functional requirements (NFRs) -- i.e. requirements that can be partially complied with -- , under dynamic and uncertain environments, provides opportunities to enhance the safety and functional correctness of systems at design time. We present a technique to formally define system attributes that can change or be changed to deal with dynamic and uncertain environments (denominated weakened specifications) as a partially ordered lattice, and to automatically explore the system under different specifications, using probabilistic model checking, to find the likelihood of satisfying a requirement. The resulting probabilities form boundaries of "optimal specifications", analogous to Pareto frontiers in multi-objective optimization, informing the designer about the system's capabilities, such as resilience or robustness, when changing its attributes to deal with dynamic and uncertain environments. We illustrate the proposed technique through a domestic robotic assistant example.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge