Focus Attention: Promoting Faithfulness and Diversity in Summarization
Paper and Code
May 25, 2021


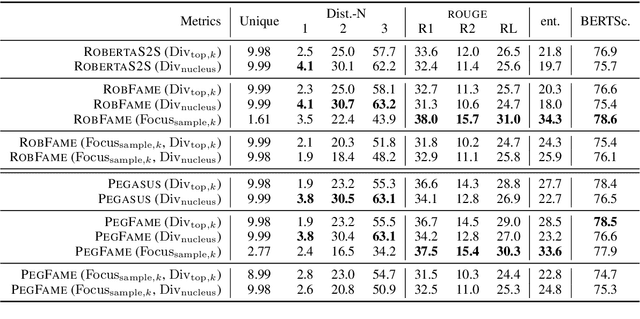
Professional summaries are written with document-level information, such as the theme of the document, in mind. This is in contrast with most seq2seq decoders which simultaneously learn to focus on salient content, while deciding what to generate, at each decoding step. With the motivation to narrow this gap, we introduce Focus Attention Mechanism, a simple yet effective method to encourage decoders to proactively generate tokens that are similar or topical to the input document. Further, we propose a Focus Sampling method to enable generation of diverse summaries, an area currently understudied in summarization. When evaluated on the BBC extreme summarization task, two state-of-the-art models augmented with Focus Attention generate summaries that are closer to the target and more faithful to their input documents, outperforming their vanilla counterparts on \rouge and multiple faithfulness measures. We also empirically demonstrate that Focus Sampling is more effective in generating diverse and faithful summaries than top-$k$ or nucleus sampling-based decoding methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge