FixyNN: Efficient Hardware for Mobile Computer Vision via Transfer Learning
Paper and Code
Feb 27, 2019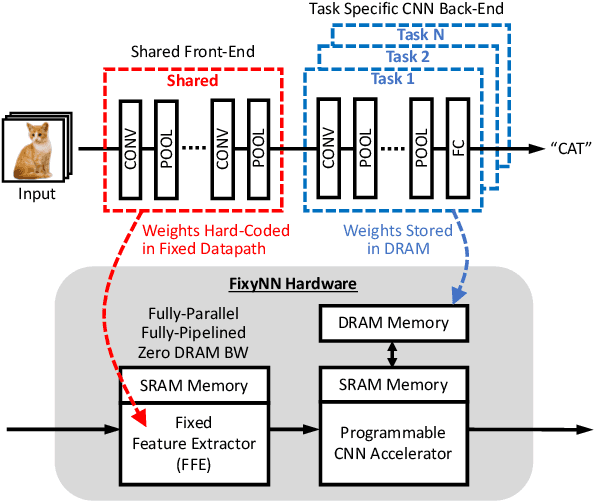
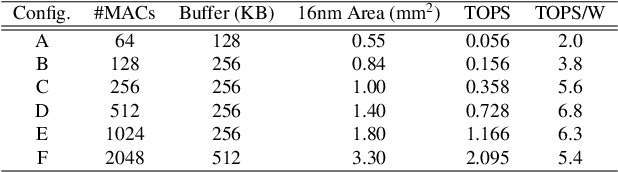
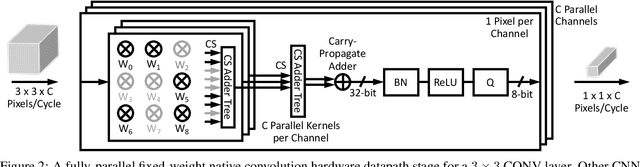
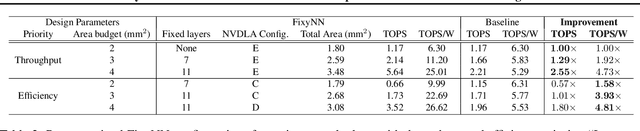
The computational demands of computer vision tasks based on state-of-the-art Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) image classification far exceed the energy budgets of mobile devices. This paper proposes FixyNN, which consists of a fixed-weight feature extractor that generates ubiquitous CNN features, and a conventional programmable CNN accelerator which processes a dataset-specific CNN. Image classification models for FixyNN are trained end-to-end via transfer learning, with the common feature extractor representing the transfered part, and the programmable part being learnt on the target dataset. Experimental results demonstrate FixyNN hardware can achieve very high energy efficiencies up to 26.6 TOPS/W ($4.81 \times$ better than iso-area programmable accelerator). Over a suite of six datasets we trained models via transfer learning with an accuracy loss of $<1\%$ resulting in up to 11.2 TOPS/W - nearly $2 \times$ more efficient than a conventional programmable CNN accelerator of the same area.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge