Fictitious GAN: Training GANs with Historical Models
Paper and Code
Jul 11, 2018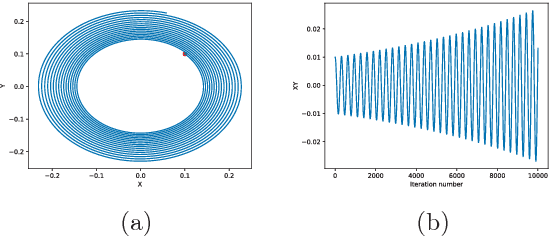
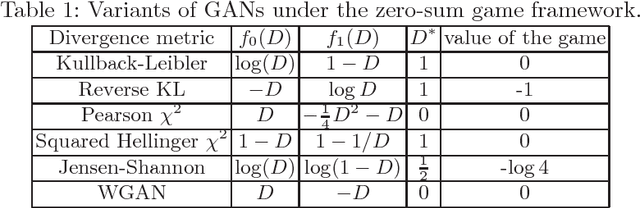
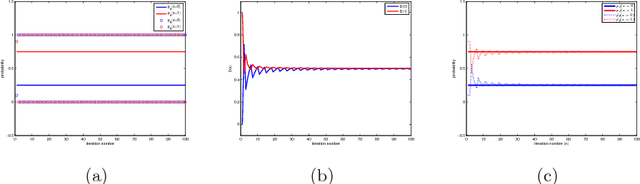
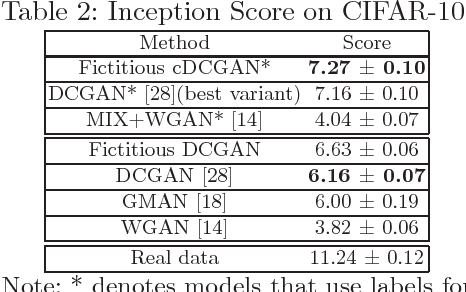
Generative adversarial networks (GANs) are powerful tools for learning generative models. In practice, the training may suffer from lack of convergence. GANs are commonly viewed as a two-player zero-sum game between two neural networks. Here, we leverage this game theoretic view to study the convergence behavior of the training process. Inspired by the fictitious play learning process, a novel training method, referred to as Fictitious GAN, is introduced. Fictitious GAN trains the deep neural networks using a mixture of historical models. Specifically, the discriminator (resp. generator) is updated according to the best-response to the mixture outputs from a sequence of previously trained generators (resp. discriminators). It is shown that Fictitious GAN can effectively resolve some convergence issues that cannot be resolved by the standard training approach. It is proved that asymptotically the average of the generator outputs has the same distribution as the data samples.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge