Feature Ranking for Semi-supervised Learning
Paper and Code
Aug 10, 2020
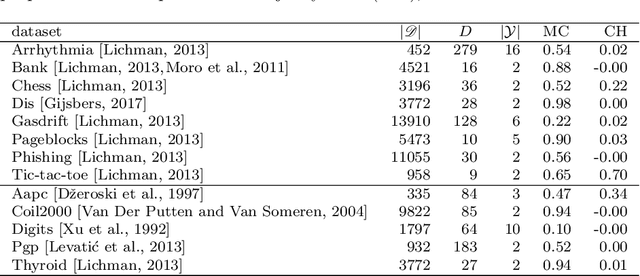
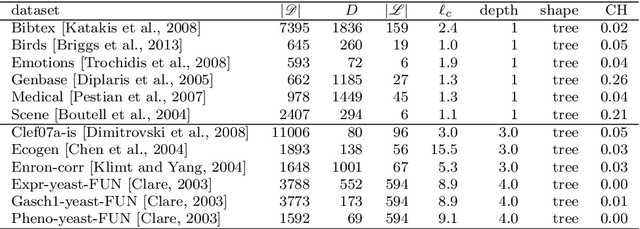
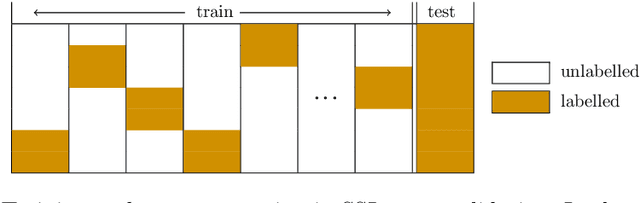
The data made available for analysis are becoming more and more complex along several directions: high dimensionality, number of examples and the amount of labels per example. This poses a variety of challenges for the existing machine learning methods: coping with dataset with a large number of examples that are described in a high-dimensional space and not all examples have labels provided. For example, when investigating the toxicity of chemical compounds there are a lot of compounds available, that can be described with information rich high-dimensional representations, but not all of the compounds have information on their toxicity. To address these challenges, we propose semi-supervised learning of feature ranking. The feature rankings are learned in the context of classification and regression as well as in the context of structured output prediction (multi-label classification, hierarchical multi-label classification and multi-target regression). To the best of our knowledge, this is the first work that treats the task of feature ranking within the semi-supervised structured output prediction context. More specifically, we propose two approaches that are based on tree ensembles and the Relief family of algorithms. The extensive evaluation across 38 benchmark datasets reveals the following: Random Forests perform the best for the classification-like tasks, while for the regression-like tasks Extra-PCTs perform the best, Random Forests are the most efficient method considering induction times across all tasks, and semi-supervised feature rankings outperform their supervised counterpart across a majority of the datasets from the different tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge