Feature Map Filtering: Improving Visual Place Recognition with Convolutional Calibration
Paper and Code
Oct 30, 2018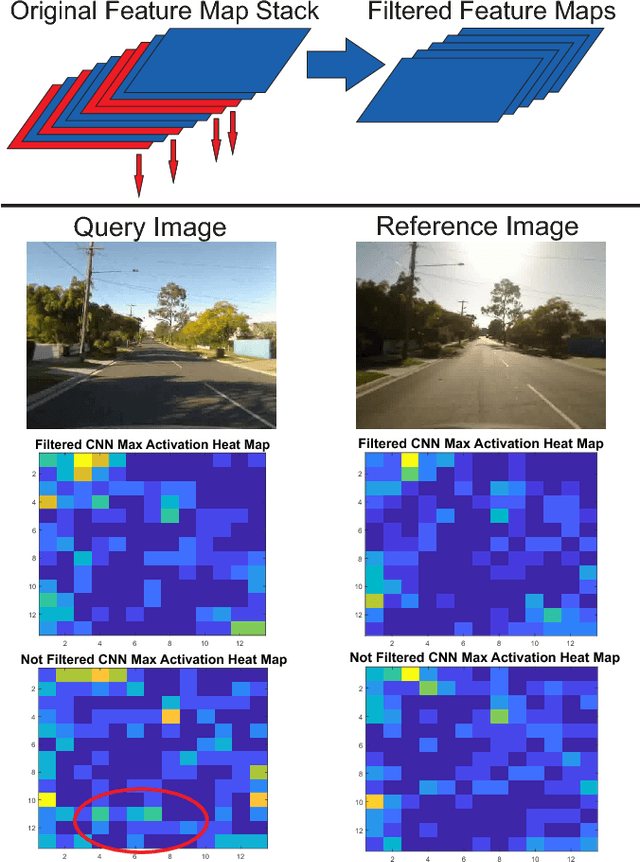
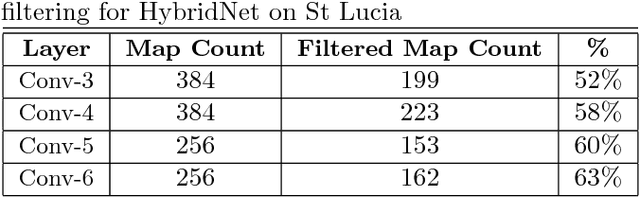
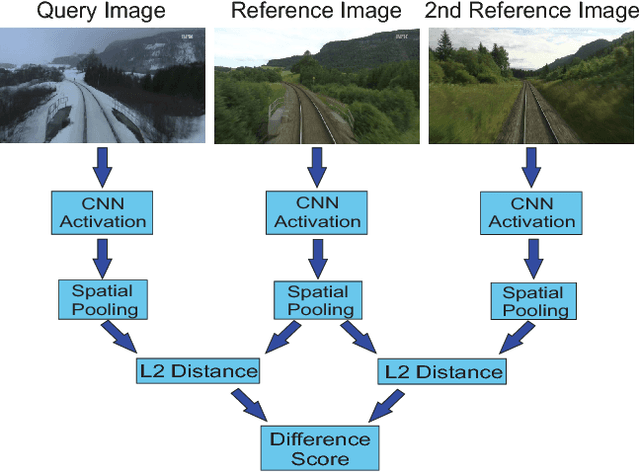
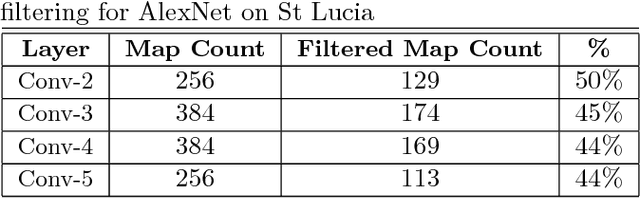
Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) have recently been shown to excel at performing visual place recognition under changing appearance and viewpoint. Previously, place recognition has been improved by intelligently selecting relevant spatial keypoints within a convolutional layer and also by selecting the optimal layer to use. Rather than extracting features out of a particular layer, or a particular set of spatial keypoints within a layer, we propose the extraction of features using a subset of the channel dimensionality within a layer. Each feature map learns to encode a different set of weights that activate for different visual features within the set of training images. We propose a method of calibrating a CNN-based visual place recognition system, which selects the subset of feature maps that best encodes the visual features that are consistent between two different appearances of the same location. Using just 50 calibration images, all collected at the beginning of the current environment, we demonstrate a significant and consistent recognition improvement across multiple layers for two different neural networks. We evaluate our proposal on three datasets with different types of appearance changes - afternoon to morning, winter to summer and night to day. Additionally, the dimensionality reduction approach improves the computational processing speed of the recognition system.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge