Fast shared response model for fMRI data
Paper and Code
Sep 27, 2019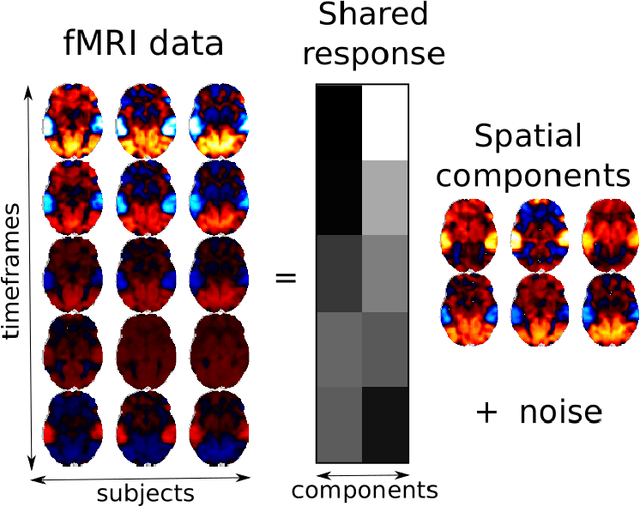

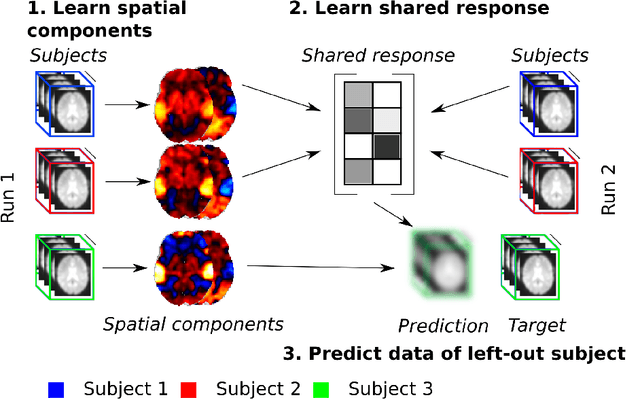
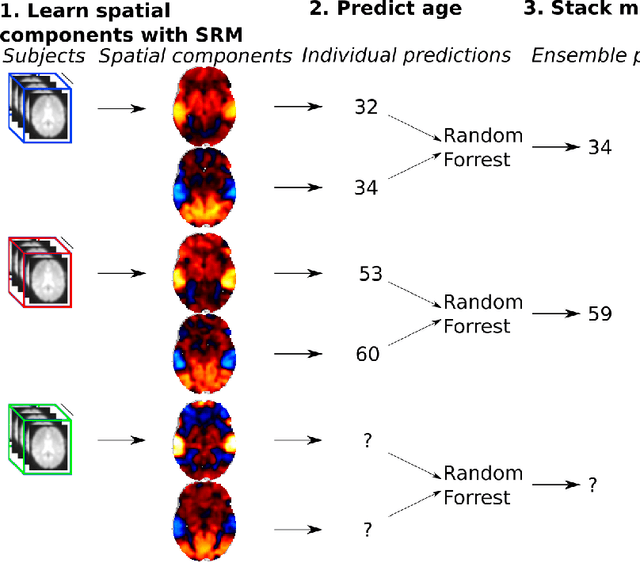
The shared response model provides a simple but effective framework toanalyse fMRI data of subjects exposed to naturalistic stimuli. However whenthe number of subjects or runs is large, fitting the model requires a large amountof memory and computational power, which limits its use in practice. In thiswork, we introduce the FastSRM algorithm that relies on an intermediate atlas-based representation. It provides considerable speed-up in time and memoryusage, hence it allows easy and fast large-scale analysis of naturalistic-stimulusfMRI data. Using four different datasets, we show that our method outperformsthe original SRM algorithm while being about 5x faster and 20x to 40x morememory efficient. Based on this contribution, we use FastSRM to predict agefrom movie watching data on the CamCAN sample. Besides delivering accuratepredictions (mean absolute error of 7.5 years), FastSRM extracts topographicpatterns that are predictive of age, demonstrating that brain activity duringfree perception reflects age.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge