FaiRR: Faithful and Robust Deductive Reasoning over Natural Language
Paper and Code
Mar 19, 2022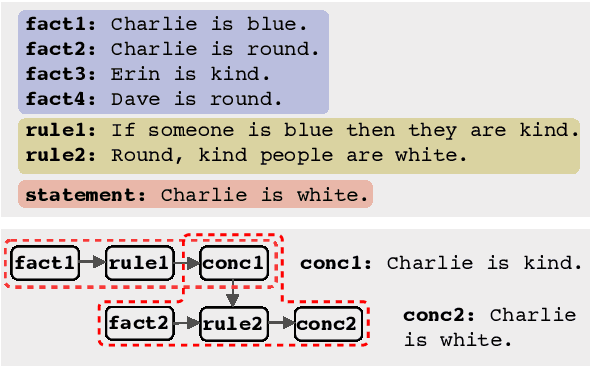
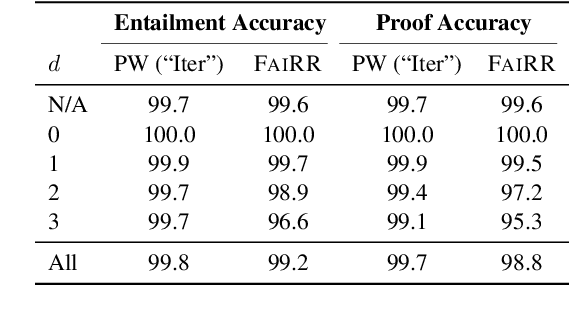
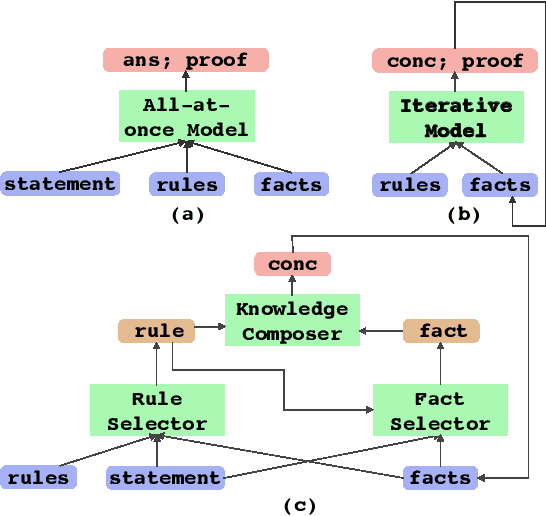
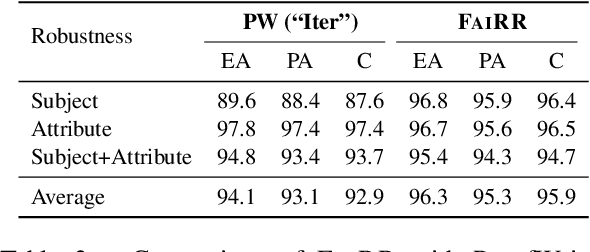
Transformers have been shown to be able to perform deductive reasoning on a logical rulebase containing rules and statements written in natural language. Recent works show that such models can also produce the reasoning steps (i.e., the proof graph) that emulate the model's logical reasoning process. Currently, these black-box models generate both the proof graph and intermediate inferences within the same model and thus may be unfaithful. In this work, we frame the deductive logical reasoning task by defining three modular components: rule selection, fact selection, and knowledge composition. The rule and fact selection steps select the candidate rule and facts to be used and then the knowledge composition combines them to generate new inferences. This ensures model faithfulness by assured causal relation from the proof step to the inference reasoning. To test our framework, we propose FaiRR (Faithful and Robust Reasoner) where the above three components are independently modeled by transformers. We observe that FaiRR is robust to novel language perturbations, and is faster at inference than previous works on existing reasoning datasets. Additionally, in contrast to black-box generative models, the errors made by FaiRR are more interpretable due to the modular approach.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge