FairAdaBN: Mitigating unfairness with adaptive batch normalization and its application to dermatological disease classification
Paper and Code
Mar 15, 2023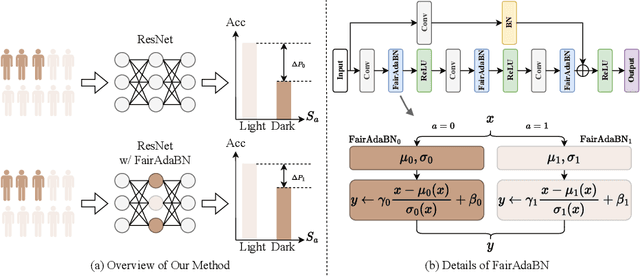
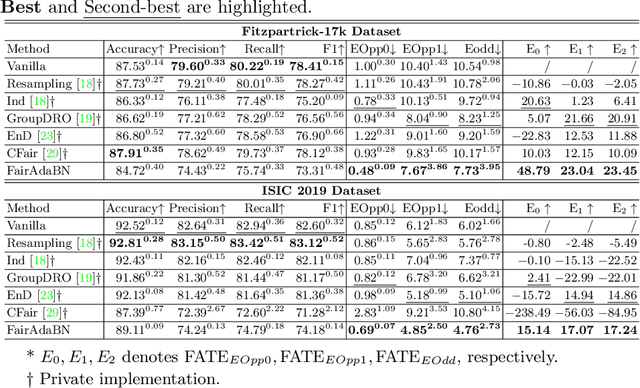
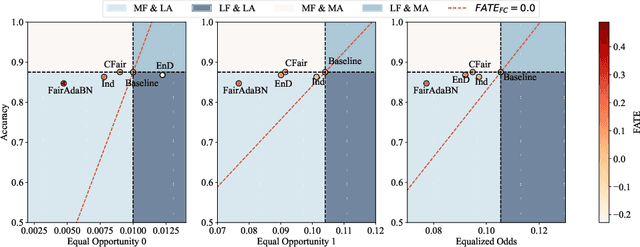
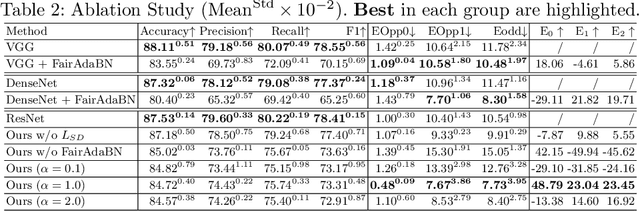
Deep learning is becoming increasingly ubiquitous in medical research and applications while involving sensitive information and even critical diagnosis decisions. Researchers observe a significant performance disparity among subgroups with different demographic attributes, which is called model unfairness, and put lots of effort into carefully designing elegant architectures to address unfairness, which poses heavy training burden, brings poor generalization, and reveals the trade-off between model performance and fairness. To tackle these issues, we propose FairAdaBN by making batch normalization adaptive to sensitive attribute. This simple but effective design can be adopted to several classification backbones that are originally unaware of fairness. Additionally, we derive a novel loss function that restrains statistical parity between subgroups on mini-batches, encouraging the model to converge with considerable fairness. In order to evaluate the trade-off between model performance and fairness, we propose a new metric, named Fairness-Accuracy Trade-off Efficiency (FATE), to compute normalized fairness improvement over accuracy drop. Experiments on two dermatological datasets show that our proposed method outperforms other methods on fairness criteria and FATE.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge