Exploring Out-of-distribution Detection for Sparse-view Computed Tomography with Diffusion Models
Paper and Code
Nov 09, 2024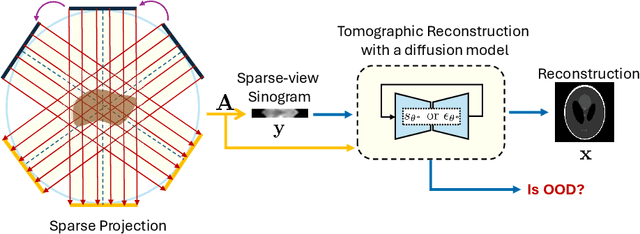
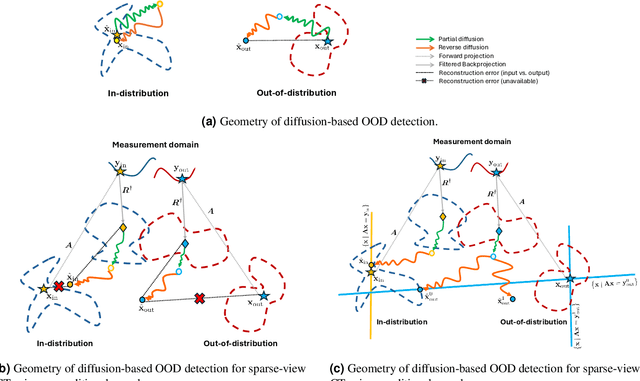
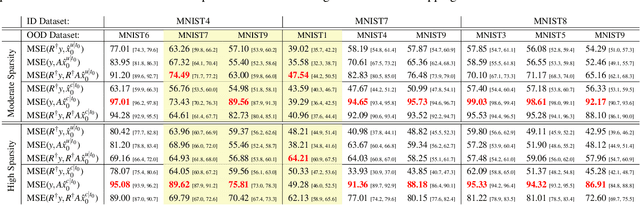

Recent works demonstrate the effectiveness of diffusion models as unsupervised solvers for inverse imaging problems. Sparse-view computed tomography (CT) has greatly benefited from these advancements, achieving improved generalization without reliance on measurement parameters. However, this comes at the cost of potential hallucinations, especially when handling out-of-distribution (OOD) data. To ensure reliability, it is essential to study OOD detection for CT reconstruction across both clinical and industrial applications. This need further extends to enabling the OOD detector to function effectively as an anomaly inspection tool. In this paper, we explore the use of a diffusion model, trained to capture the target distribution for CT reconstruction, as an in-distribution prior. Building on recent research, we employ the model to reconstruct partially diffused input images and assess OOD-ness through multiple reconstruction errors. Adapting this approach for sparse-view CT requires redefining the notions of "input" and "reconstruction error". Here, we use filtered backprojection (FBP) reconstructions as input and investigate various definitions of reconstruction error. Our proof-of-concept experiments on the MNIST dataset highlight both successes and failures, demonstrating the potential and limitations of integrating such an OOD detector into a CT reconstruction system. Our findings suggest that effective OOD detection can be achieved by comparing measurements with forward-projected reconstructions, provided that reconstructions from noisy FBP inputs are conditioned on the measurements. However, conditioning can sometimes lead the OOD detector to inadvertently reconstruct OOD images well. To counter this, we introduce a weighting approach that improves robustness against highly informative OOD measurements, albeit with a trade-off in performance in certain cases.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge