Exploring Multitask Learning for Low-Resource AbstractiveSummarization
Paper and Code
Sep 17, 2021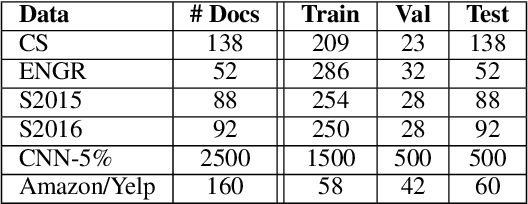



This paper explores the effect of using multitask learning for abstractive summarization in the context of small training corpora. In particular, we incorporate four different tasks (extractive summarization, language modeling, concept detection, and paraphrase detection) both individually and in combination, with the goal of enhancing the target task of abstractive summarization via multitask learning. We show that for many task combinations, a model trained in a multitask setting outperforms a model trained only for abstractive summarization, with no additional summarization data introduced. Additionally, we do a comprehensive search and find that certain tasks (e.g. paraphrase detection) consistently benefit abstractive summarization, not only when combined with other tasks but also when using different architectures and training corpora.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge