Exploratory Factor Analysis of Data on a Sphere
Paper and Code
Nov 09, 2021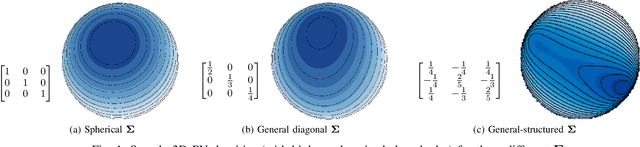
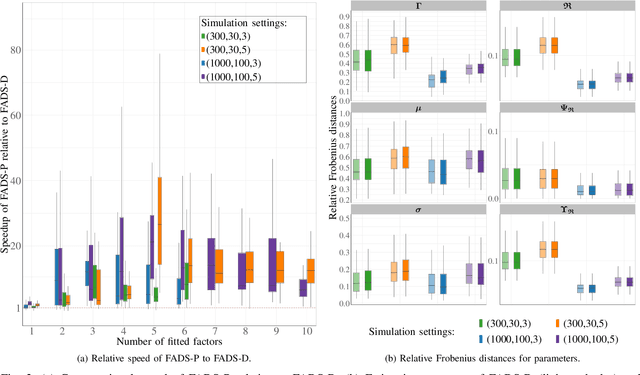
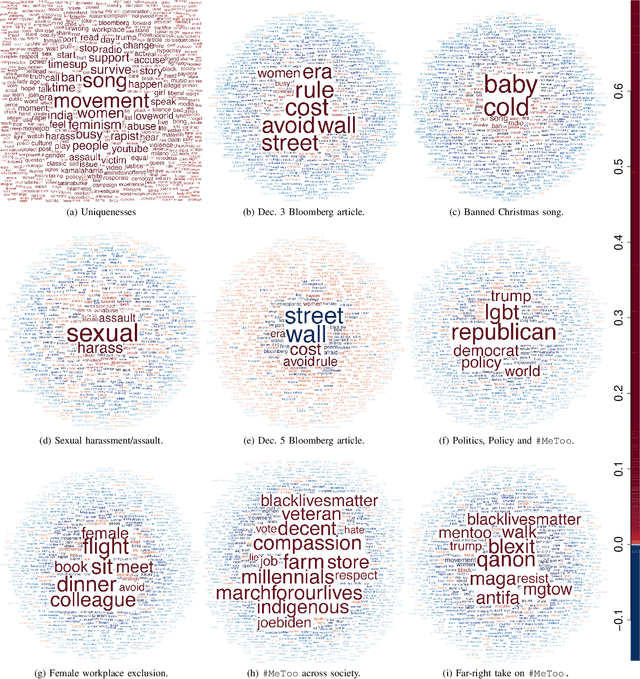
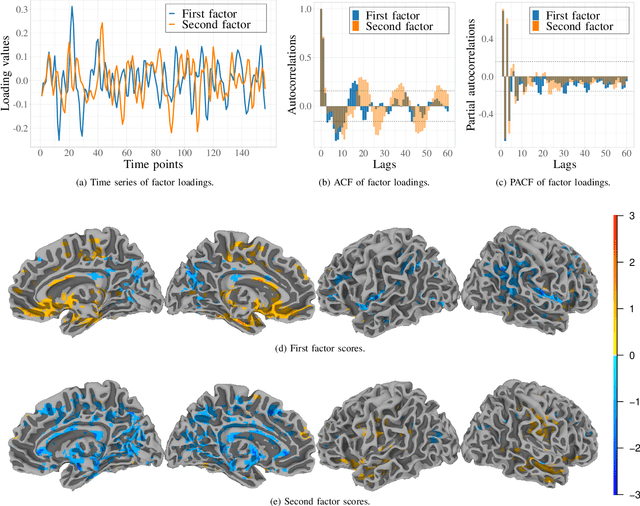
Data on high-dimensional spheres arise frequently in many disciplines either naturally or as a consequence of preliminary processing and can have intricate dependence structure that needs to be understood. We develop exploratory factor analysis of the projected normal distribution to explain the variability in such data using a few easily interpreted latent factors. Our methodology provides maximum likelihood estimates through a novel fast alternating expectation profile conditional maximization algorithm. Results on simulation experiments on a wide range of settings are uniformly excellent. Our methodology provides interpretable and insightful results when applied to tweets with the $\#MeToo$ hashtag in early December 2018, to time-course functional Magnetic Resonance Images of the average pre-teen brain at rest, to characterize handwritten digits, and to gene expression data from cancerous cells in the Cancer Genome Atlas.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge