Exploiting the Power of Levenberg-Marquardt Optimizer with Anomaly Detection in Time Series
Paper and Code
Nov 11, 2021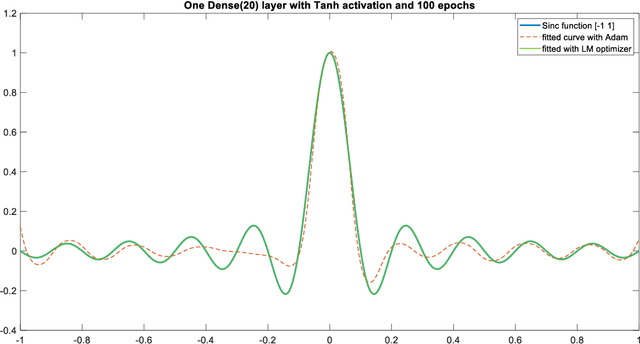
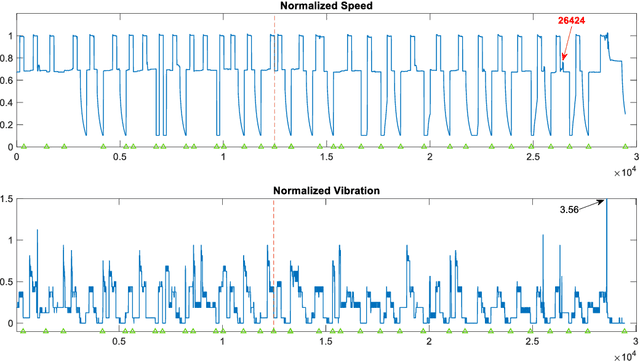
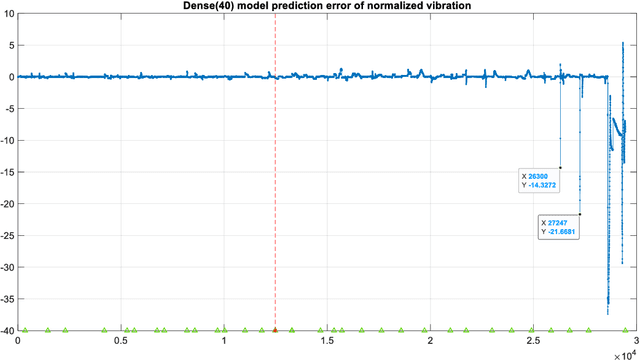
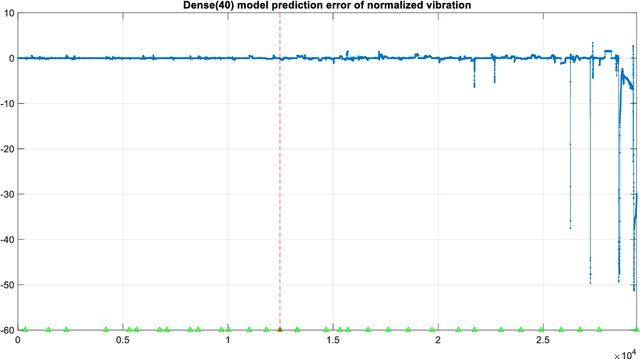
The Levenberg-Marquardt (LM) optimization algorithm has been widely used for solving machine learning problems. Literature reviews have shown that the LM can be very powerful and effective on moderate function approximation problems when the number of weights in the network is not more than a couple of hundred. In contrast, the LM does not seem to perform as well when dealing with pattern recognition or classification problems, and inefficient when networks become large (e.g. with more than 500 weights). In this paper, we exploit the true power of LM algorithm using some real world aircraft datasets. On these datasets most other commonly used optimizers are unable to detect the anomalies caused by the changing conditions of the aircraft engine. The challenging nature of the datasets are the abrupt changes in the time series data. We find that the LM optimizer has a much better ability to approximate abrupt changes and detect anomalies than other optimizers. We compare the performance, in addressing this anomaly/change detection problem, of the LM and several other optimizers. We assess the relative performance based on a range of measures including network complexity (i.e. number of weights), fitting accuracy, over fitting, training time, use of GPUs and memory requirement etc. We also discuss the issue of robust LM implementation in MATLAB and Tensorflow for promoting more popular usage of the LM algorithm and potential use of LM optimizer for large-scale problems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge