Exploiting Record Similarity for Practical Vertical Federated Learning
Paper and Code
Jun 11, 2021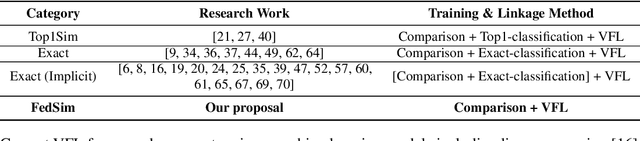

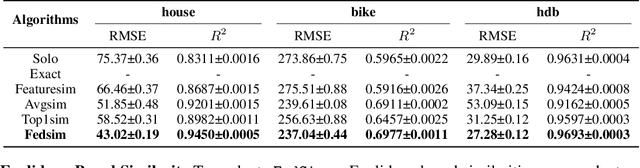
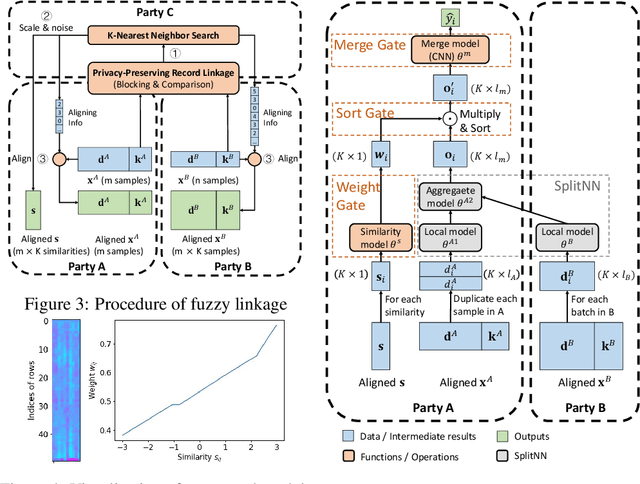
As the privacy of machine learning has drawn increasing attention, federated learning is introduced to enable collaborative learning without revealing raw data. Notably, \textit{vertical federated learning} (VFL), where parties share the same set of samples but only hold partial features, has a wide range of real-world applications. However, existing studies in VFL rarely study the ``record linkage'' process. They either design algorithms assuming the data from different parties have been linked or use simple linkage methods like exact-linkage or top1-linkage. These approaches are unsuitable for many applications, such as the GPS location and noisy titles requiring fuzzy matching. In this paper, we design a novel similarity-based VFL framework, FedSim, which is suitable for more real-world applications and achieves higher performance on traditional VFL tasks. Moreover, we theoretically analyze the privacy risk caused by sharing similarities. Our experiments on three synthetic datasets and five real-world datasets with various similarity metrics show that FedSim consistently outperforms other state-of-the-art baselines.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge