Explanations of Machine Learning predictions: a mandatory step for its application to Operational Processes
Paper and Code
Dec 30, 2020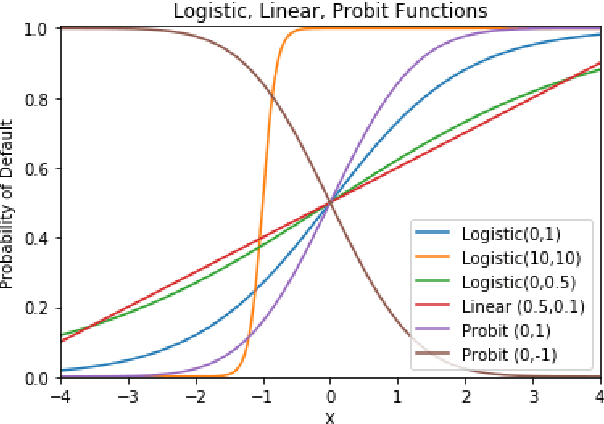
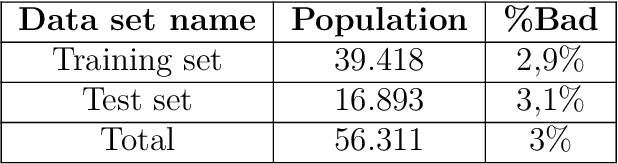
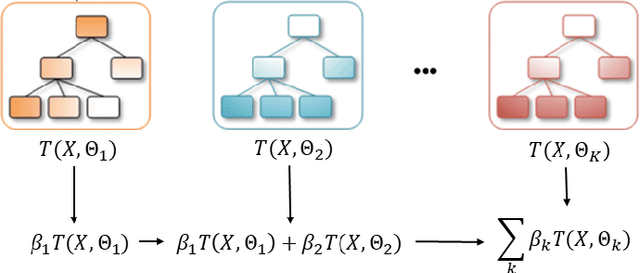
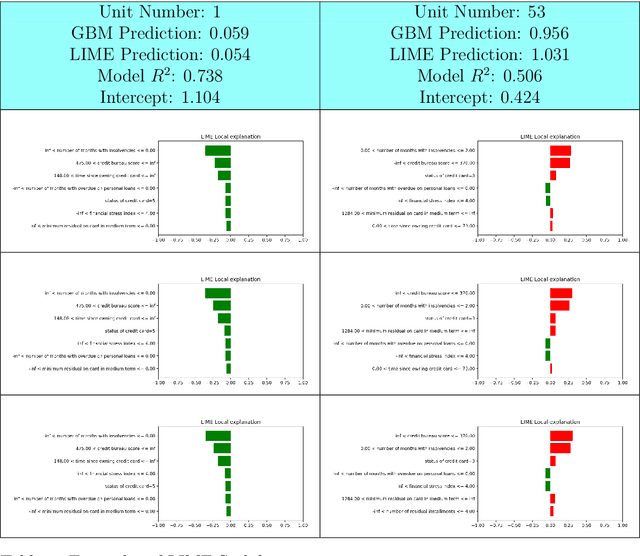
In the global economy, credit companies play a central role in economic development, through their activity as money lenders. This important task comes with some drawbacks, mainly the risk of the debtors not being able to repay the provided credit. Therefore, Credit Risk Modelling (CRM), namely the evaluation of the probability that a debtor will not repay the due amount, plays a paramount role. Statistical approaches have been successfully exploited since long, becoming the most used methods for CRM. Recently, also machine and deep learning techniques have been applied to the CRM task, showing an important increase in prediction quality and performances. However, such techniques usually do not provide reliable explanations for the scores they come up with. As a consequence, many machine and deep learning techniques fail to comply with western countries' regulations such as, for example, GDPR. In this paper we suggest to use LIME (Local Interpretable Model-agnostic Explanations) technique to tackle the explainability problem in this field, we show its employment on a real credit-risk dataset and eventually discuss its soundness and the necessary improvements to guarantee its adoption and compliance with the task.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge