Explain, Adapt and Retrain: How to improve the accuracy of a PPM classifier through different explanation styles
Paper and Code
Mar 27, 2023


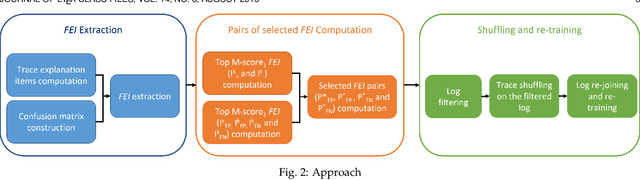
Recent papers have introduced a novel approach to explain why a Predictive Process Monitoring (PPM) model for outcome-oriented predictions provides wrong predictions. Moreover, they have shown how to exploit the explanations, obtained using state-of-the art post-hoc explainers, to identify the most common features that induce a predictor to make mistakes in a semi-automated way, and, in turn, to reduce the impact of those features and increase the accuracy of the predictive model. This work starts from the assumption that frequent control flow patterns in event logs may represent important features that characterize, and therefore explain, a certain prediction. Therefore, in this paper, we (i) employ a novel encoding able to leverage DECLARE constraints in Predictive Process Monitoring and compare the effectiveness of this encoding with Predictive Process Monitoring state-of-the art encodings, in particular for the task of outcome-oriented predictions; (ii) introduce a completely automated pipeline for the identification of the most common features inducing a predictor to make mistakes; and (iii) show the effectiveness of the proposed pipeline in increasing the accuracy of the predictive model by validating it on different real-life datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge