Experiments with mmWave Automotive Radar Test-bed
Paper and Code
Dec 29, 2019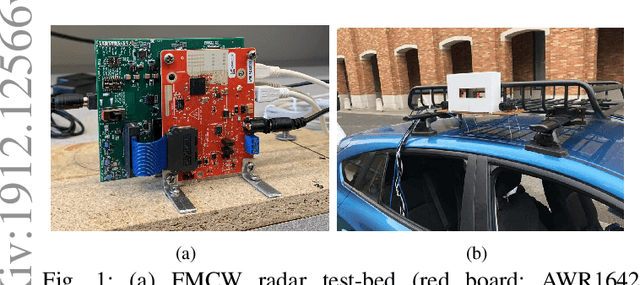
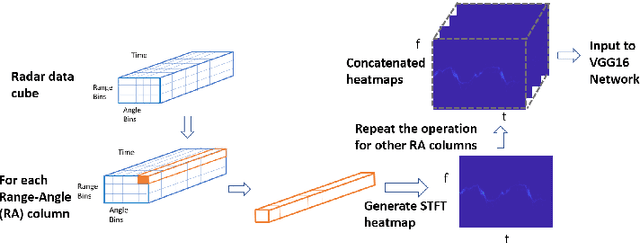
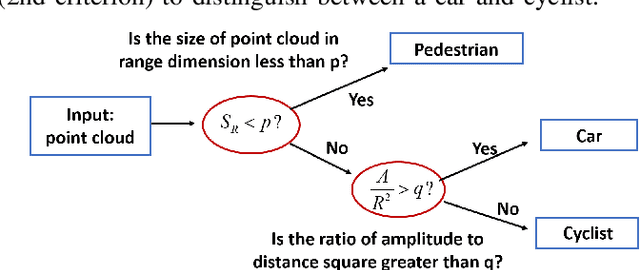
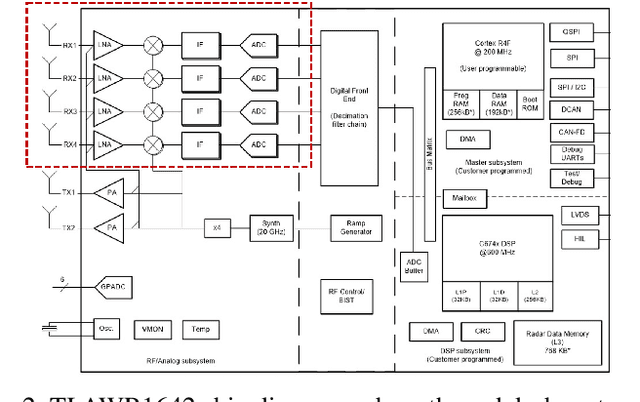
Millimeter-wave (mmW) radars are being increasingly integrated in commercial vehicles to support new Adaptive Driver Assisted Systems (ADAS) for its ability to provide high accuracy location, velocity, and angle estimates of objects, largely independent of environmental conditions. Such radar sensors not only perform basic functions such as detection and ranging/angular localization, but also provide critical inputs for environmental perception via object recognition and classification. To explore radar-based ADAS applications, we have assembled a lab-scale frequency modulated continuous wave (FMCW) radar test-bed (https://depts.washington.edu/funlab/research) based on Texas Instrument's (TI) automotive chipset family. In this work, we describe the test-bed components and provide a summary of FMCW radar operational principles. To date, we have created a large raw radar dataset for various objects under controlled scenarios. Thereafter, we apply some radar imaging algorithms to the collected dataset, and present some preliminary results that validate its capabilities in terms of object recognition.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge