Experimental Demonstration of Array-level Learning with Phase Change Synaptic Devices
Paper and Code
Jun 03, 2014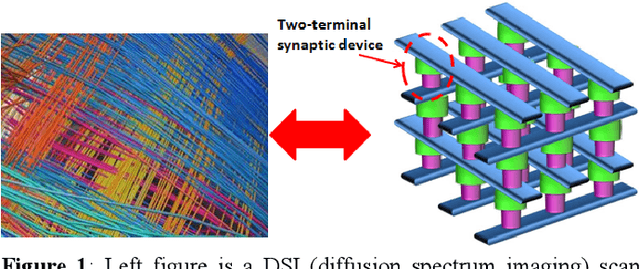
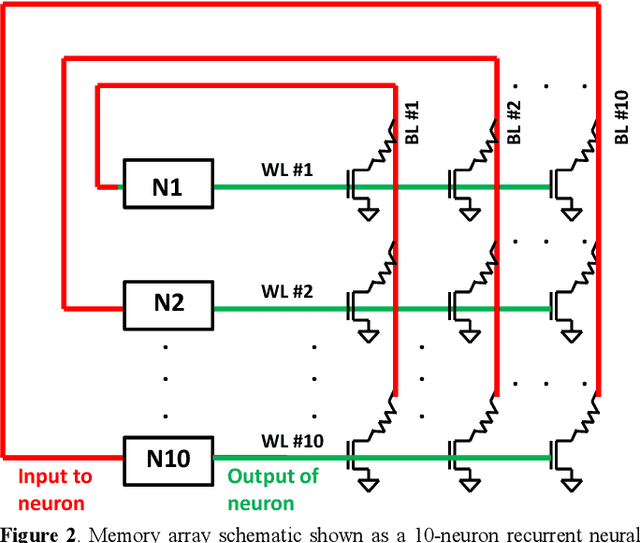
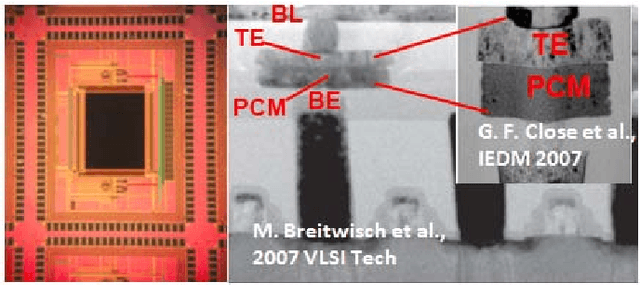
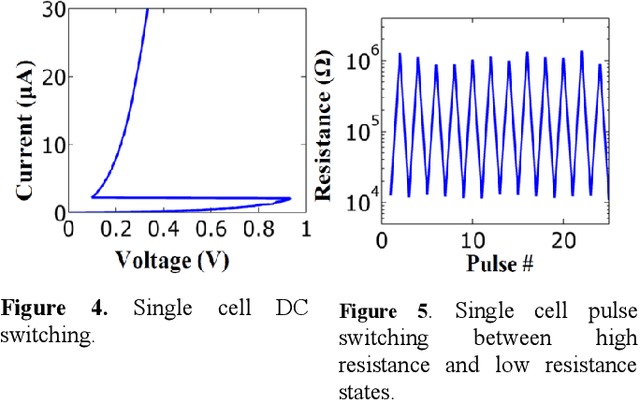
The computational performance of the biological brain has long attracted significant interest and has led to inspirations in operating principles, algorithms, and architectures for computing and signal processing. In this work, we focus on hardware implementation of brain-like learning in a brain-inspired architecture. We demonstrate, in hardware, that 2-D crossbar arrays of phase change synaptic devices can achieve associative learning and perform pattern recognition. Device and array-level studies using an experimental 10x10 array of phase change synaptic devices have shown that pattern recognition is robust against synaptic resistance variations and large variations can be tolerated by increasing the number of training iterations. Our measurements show that increase in initial variation from 9 % to 60 % causes required training iterations to increase from 1 to 11.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge