Evolutionary Diversity Optimisation for The Traveling Thief Problem
Paper and Code
Apr 06, 2022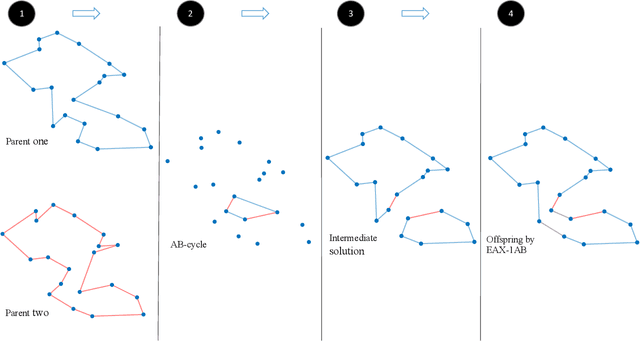
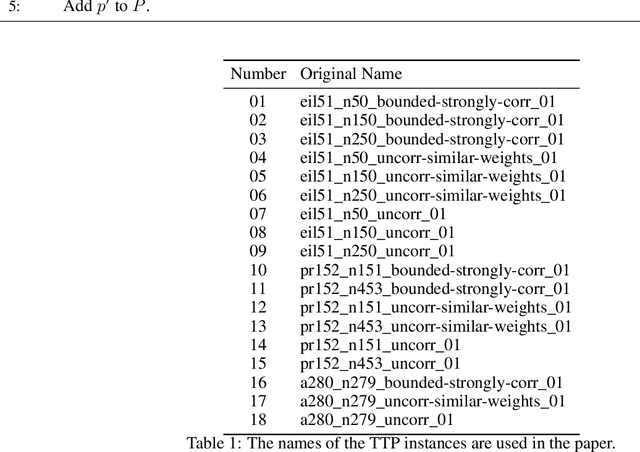


There has been a growing interest in the evolutionary computation community to compute a diverse set of high-quality solutions for a given optimisation problem. This can provide the practitioners with invaluable information about the solution space and robustness against imperfect modelling and minor problems' changes. It also enables the decision-makers to involve their interests and choose between various solutions. In this study, we investigate for the first time a prominent multi-component optimisation problem, namely the Traveling Thief Problem (TTP), in the context of evolutionary diversity optimisation. We introduce a bi-level evolutionary algorithm to maximise the structural diversity of the set of solutions. Moreover, we examine the inter-dependency among the components of the problem in terms of structural diversity and empirically determine the best method to obtain diversity. We also conduct a comprehensive experimental investigation to examine the introduced algorithm and compare the results to another recently introduced framework based on the use of Quality Diversity (QD). Our experimental results show a significant improvement of the QD approach in terms of structural diversity for most TTP benchmark instances.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge