Evaluation of self-supervised pre-training for automatic infant movement classification using wearable movement sensors
Paper and Code
May 16, 2023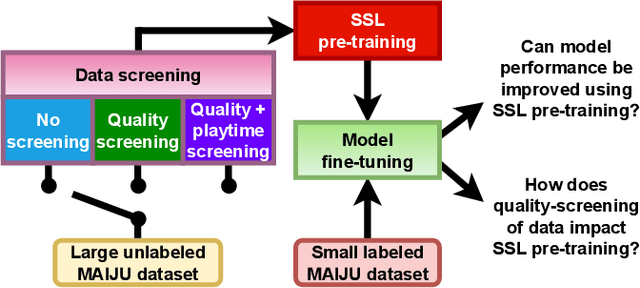
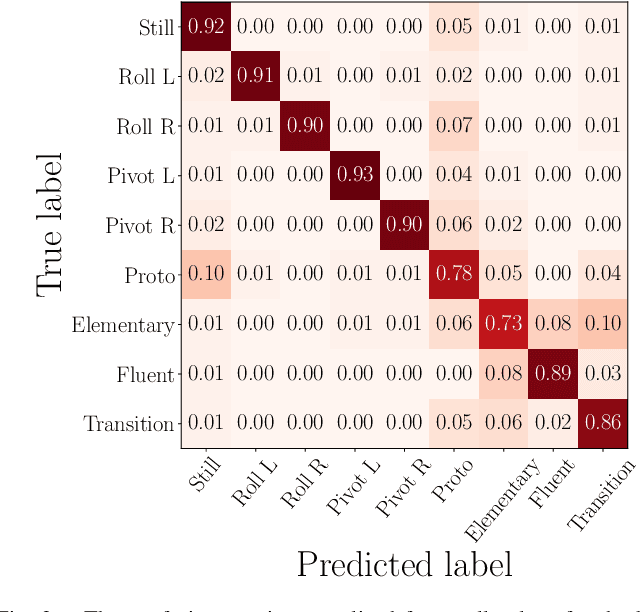
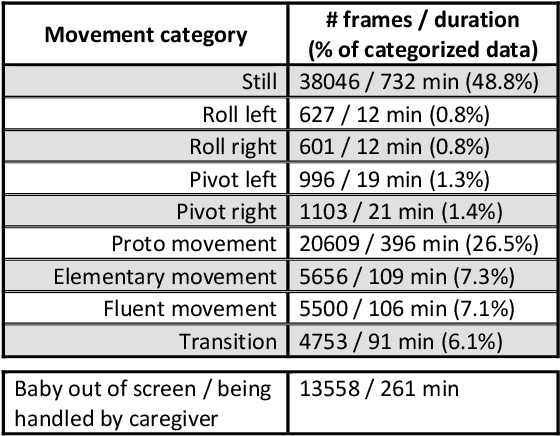
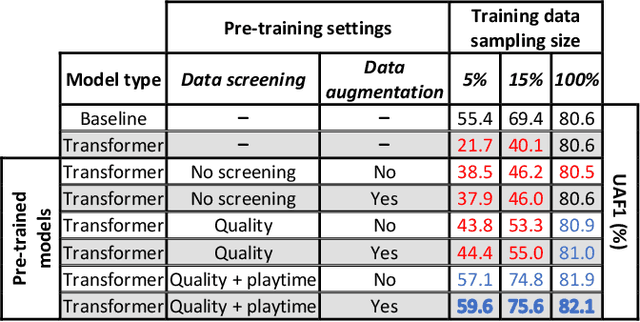
The recently-developed infant wearable MAIJU provides a means to automatically evaluate infants' motor performance in an objective and scalable manner in out-of-hospital settings. This information could be used for developmental research and to support clinical decision-making, such as detection of developmental problems and guiding of their therapeutic interventions. MAIJU-based analyses rely fully on the classification of infant's posture and movement; it is hence essential to study ways to increase the accuracy of such classifications, aiming to increase the reliability and robustness of the automated analysis. Here, we investigated how self-supervised pre-training improves performance of the classifiers used for analyzing MAIJU recordings, and we studied whether performance of the classifier models is affected by context-selective quality-screening of pre-training data to exclude periods of little infant movement or with missing sensors. Our experiments show that i) pre-training the classifier with unlabeled data leads to a robust accuracy increase of subsequent classification models, and ii) selecting context-relevant pre-training data leads to substantial further improvements in the classifier performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge