Evaluation of RF Fingerprinting-Aided RSS-Based Target Localization for Emergency Response
Paper and Code
Jun 19, 2022
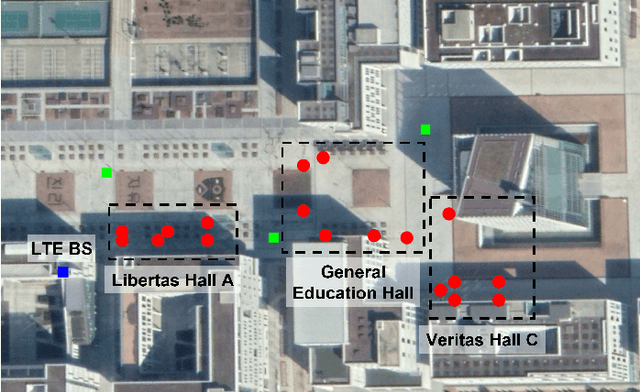

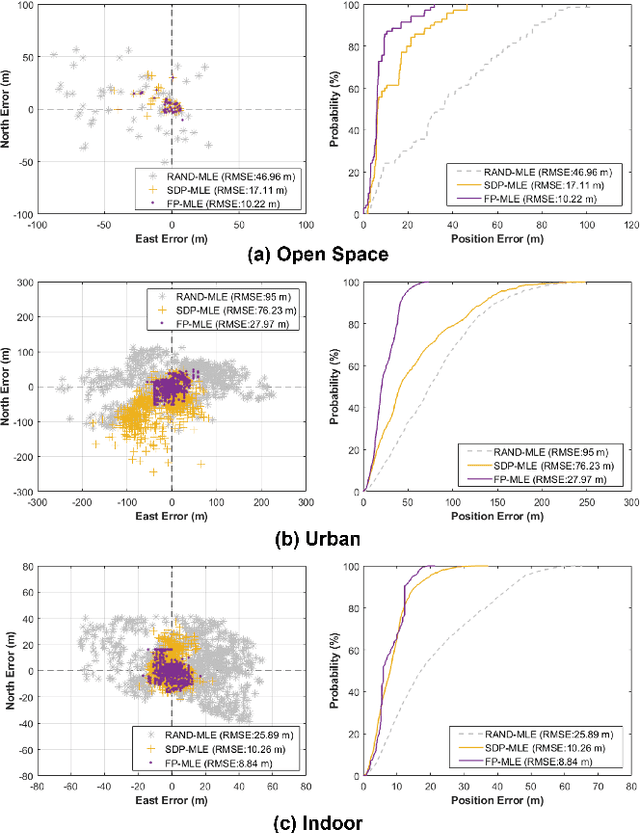
Target localization is essential for emergency dispatching situations. Maximum likelihood estimation (MLE) methods are widely used to estimate the target position based on the received signal strength measurements. However, the performance of MLE solvers is significantly affected by the initialization (i.e., initial guess of the solution or solution search space). To address this, a previous study proposed the semidefinite programming (SDP)-based MLE initialization. However, the performance of the SDP-based initialization technique is largely affected by the shadowing variance and geometric diversity between the target and receivers. In this study, a radio frequency (RF) fingerprinting-based MLE initialization is proposed. Further, a maximum likelihood problem for target localization combining RF fingerprinting is formulated. In the three test environments of open space, urban, and indoor, the proposed RF fingerprinting-aided target localization method showed a performance improvement of up to 63.31% and an average of 39.13%, compared to the MLE algorithm initialized with SDP. Furthermore, unlike the SDP-MLE method, the proposed method was not significantly affected by the poor geometry between the target and receivers in our experiments.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge