Evaluating Neural Word Representations in Tensor-Based Compositional Settings
Paper and Code
Aug 26, 2014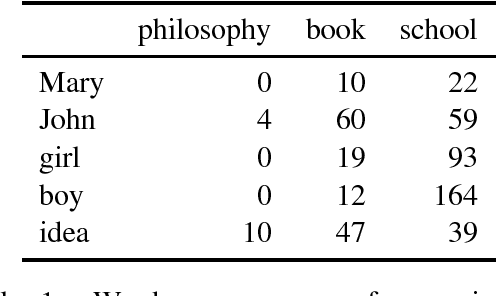

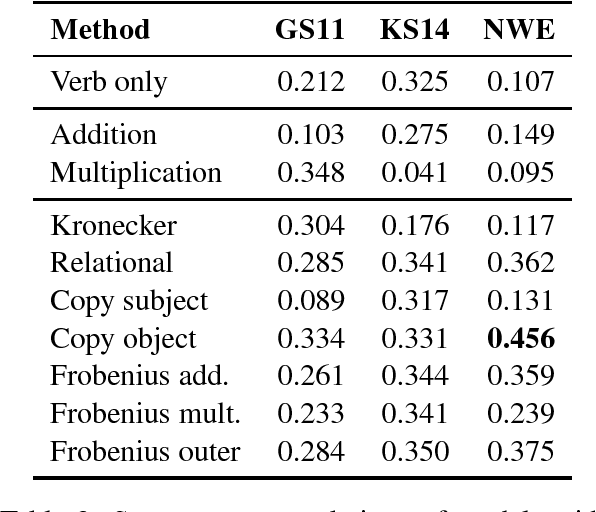

We provide a comparative study between neural word representations and traditional vector spaces based on co-occurrence counts, in a number of compositional tasks. We use three different semantic spaces and implement seven tensor-based compositional models, which we then test (together with simpler additive and multiplicative approaches) in tasks involving verb disambiguation and sentence similarity. To check their scalability, we additionally evaluate the spaces using simple compositional methods on larger-scale tasks with less constrained language: paraphrase detection and dialogue act tagging. In the more constrained tasks, co-occurrence vectors are competitive, although choice of compositional method is important; on the larger-scale tasks, they are outperformed by neural word embeddings, which show robust, stable performance across the tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge