Evaluating Machine Translation Performance on Chinese Idioms with a Blacklist Method
Paper and Code
Feb 20, 2018
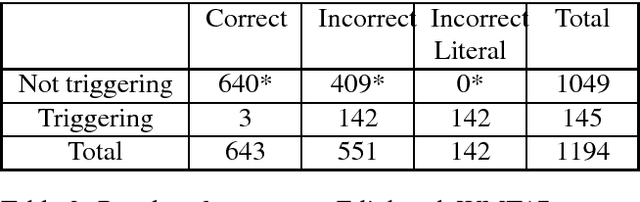
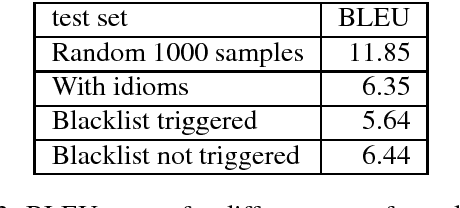
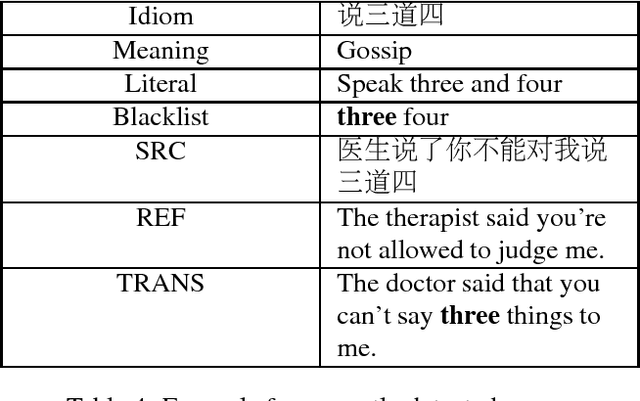
Idiom translation is a challenging problem in machine translation because the meaning of idioms is non-compositional, and a literal (word-by-word) translation is likely to be wrong. In this paper, we focus on evaluating the quality of idiom translation of MT systems. We introduce a new evaluation method based on an idiom-specific blacklist of literal translations, based on the insight that the occurrence of any blacklisted words in the translation output indicates a likely translation error. We introduce a dataset, CIBB (Chinese Idioms Blacklists Bank), and perform an evaluation of a state-of-the-art Chinese-English neural MT system. Our evaluation confirms that a sizable number of idioms in our test set are mistranslated (46.1%), that literal translation error is a common error type, and that our blacklist method is effective at identifying literal translation errors.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge